Colon diverticula
| Normal anatomy |
|
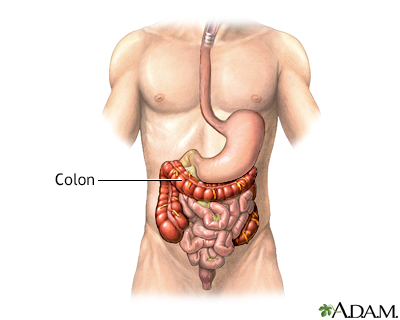
The colon, or large intestine, is a muscular tube that begins at the end of the small intestine and runs to the rectum. The colon absorbs water from liquid stool that is delivered to it from the small intestine.
|
|
| Indications, part 1 |
|
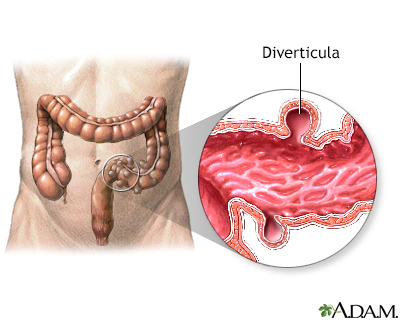
Diverticula are out-pouchings of the wall of the colon. They are thought to be the result of a diet low in fiber. By the age of 60, over half of all Americans have colonic diverticula.
|
|
| Indications, part 2 |
|
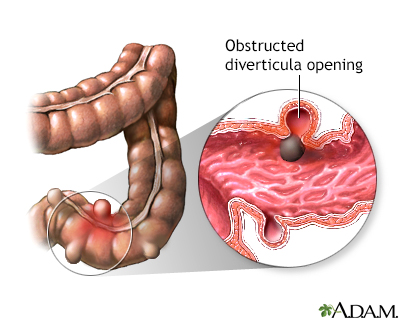
In most cases, diverticula go unnoticed. However, in a small percentage of patients, diverticula can cause problems. The most common problem is diverticulitis, which occurs when a small, hard piece of stool is trapped in the opening of the diverticula. This leads to inflammation and sometimes death of the segment of colon containing the diverticula.
|
|
| Indications, part 3 |
|
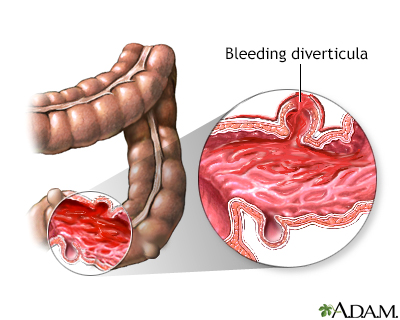
Diverticula can also bleed and cause significant blood loss from the gastrointestinal tract. Vessels overlying a diverticula are stretched until they break, causing bleeding into the colon. Blood is usually passed in the stool.
|
|
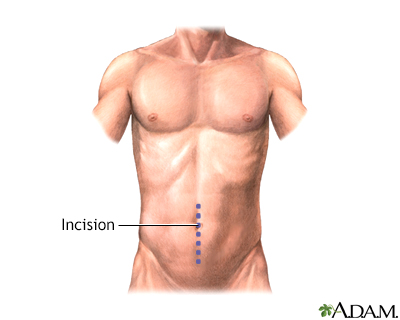
| Incision |
|
Treatment of complicated diverticulitis and diverticular bleeding may involve surgical removal of the segment of colon containing the diverticula. While the patient is deep asleep and pain free (general anesthesia), an incision is made in the midline of the abdomen.
|
|
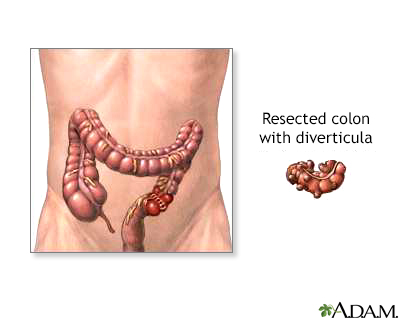
| Procedure |
|
After the diseased area is removed, the healthy ends of the colon are sewn back together. Occasionally, especially in cases of diverticulitis, where there is significant inflammation, a colostomy is performed. After the inflammation has resided, the colostomy is removed and the healthy ends of the colon are sewn back together.
|
|

|
Review Date:
5/14/2024
Reviewed By:
Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
© 1997-

All rights reserved.