Lung transplant
| Normal anatomy |
|
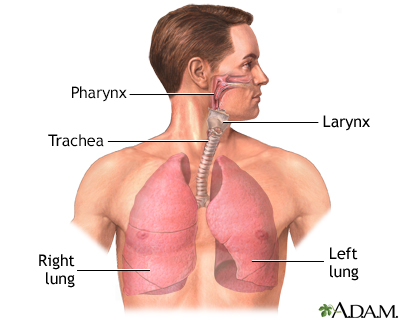
The lungs, which reside in the thorax, or chest cavity, act as a site for oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange for the blood.
|
|
| Indication |
|
Lung transplants may be recommended for patients with severe lung disease such as:
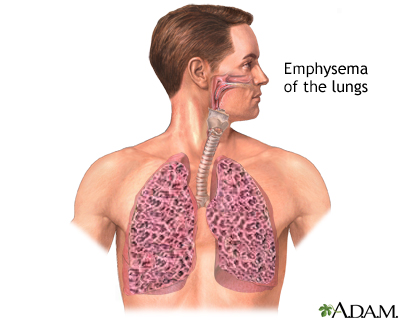
- Permanent enlargement of air sacs (alveoli) with loss of ability to completely exhale (emphysema)
- Hereditary lung blockages (cystic fibrosis)
- Long-term (chronic) infections (sarcoidosis)
- Permanent scarring and thickening of lung tissue (idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis)
|
|
| Incision |
|
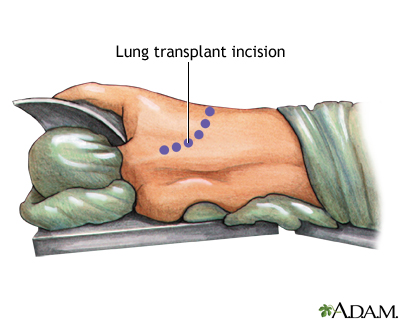
While the patient is deep asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia), an incision is made through the breast bone (sternum). One or two donor lungs are transplanted, depending on the diease process being treated.
|
|
| Procedure |
|
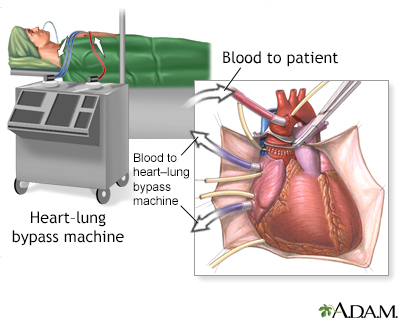
Tubes are used to re-route the blood to a heart-lung bypass machine to keep the blood oxygenated and circulating during the surgery.
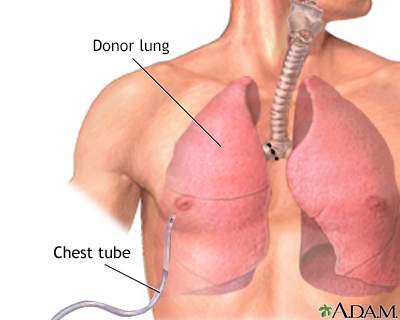
The patient's lungs are removed and the donor lungs are stitched into place. Drainage tubes (chest tubes) are inserted to drain air, fluid, and blood out of the chest for several days to allow the lungs to fully re-expand.
|
|
| Aftercare |
|
The patient's lungs are removed and the donor lungs are stitched into place. Drainage tubes (chest tubes) are inserted to drain air, fluid, and blood out of the chest for several days to allow the lungs to fully re-expand.
Patients will require immunosuppressive medications for the rest of their lives to prevent immune rejection of the transplanted lung. Lung transplantation results vary depending on the disease being treated and the experience of the center performing the surgery.
|
|

|
Review Date:
4/1/2025
Reviewed By:
John Meilahn, MD, General Surgeon, Wyndmoor, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
© 1997-

All rights reserved.