Scar revision
| Normal anatomy |
|
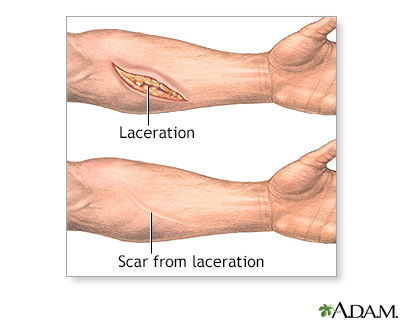
Skin covers the entire body, and acts as a protective barrier. Scar tissue forms as skin heals after an injury (such as an accident) or surgery. The amount of scarring may be determined by the size, depth, and location of the wound; the age of the person; heredity; and skin characteristics including color (pigmentation).
No scar can be removed completely. The degree of improvement will depend on variables such as the direction and size of the scar, the age of the person, skin type and color, and hereditary factors that may precondition the extent of the healing process.
|
|
| Indication |
|
Scar removal and revision is best performed after months or years of healing. Medications (topical corticosteroids, anesthetic ointments, and antihistamine creams) can reduce the symptoms of itching and tenderness during this time. Scars shrink and becomes less noticeable as they age, therefore, immediate surgical revision is delayed until the scar lightens in color, which is usually several months or even a year after a wound has healed.
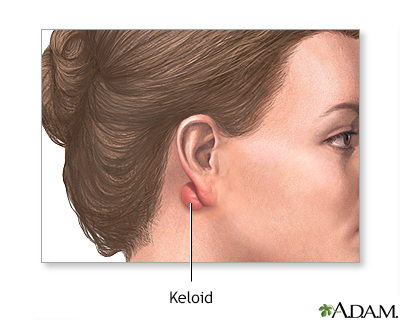
A keloid is an abnormal scar that is thicker, different color and texture, extends beyond the edge of the wound, and has a tendency to recur. It often creates a thick, puckered effect simulating a tumor. Keloids are removed at the point where it meets normal tissue. The skin is then sutured closed. Keloids often recur at the site of scar revision.
|
|
| Procedure |
|
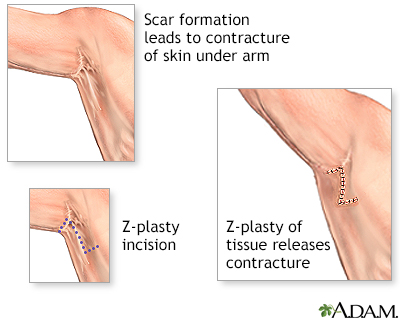
Surgery to revise scars is done while the patient is awake, sleeping (sedated), or deep asleep and pain-free (local anesthesia or general anesthesia). Massive injuries (such as burns) can cause loss of a large area of skin and may form hypertrophic scars. A hypertrophic scar can cause restricted movement of muscles, joints, and tendons (contracture). Surgical repair includes removing excessive scar tissue and a series of small incisions on both sides of the scar site, which create V-shaped skin flaps (Z-plasty) may be used. The result is a thin, less noticeable scar because the wound closure following a Z-plasty more closely follows the natural skin folds.
|
|
| Procedure |
|
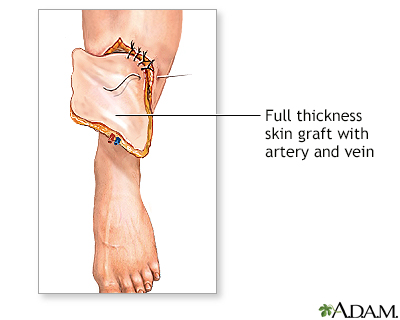
Skin grafting involves the taking a thin (split thickness) layer of skin from another part of the body and placing it over the injured area. Skin flap surgery involves moving an entire thickness (full thickness) of skin, fat, nerves, blood vessels, and muscle from a healthy part of the body to the injured site. These techniques are planned when a considerable amount of skin has been lost in the original injury, when a thin scar will not heal, and when improved function (rather than aesthetic reasons) are the primary concern. Secondary procedures may later be necessary to achieve appropriate aesthetic results.
|
|

Review Date:
5/6/2025
Reviewed By:
Tang Ho, MD, Associate Professor, Division of Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, The University of Texas Medical School at Houston, Houston, TX. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
© 1997-

All rights reserved.