Cervical dysplasia
| Normal anatomy |
|
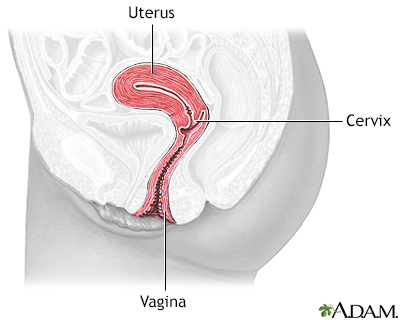
The cervix is the tissue that leads from the uterus into the vagina.
|
|
| Indications |
|
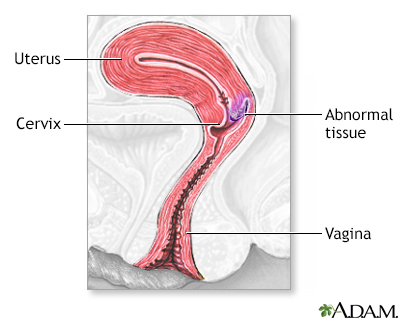
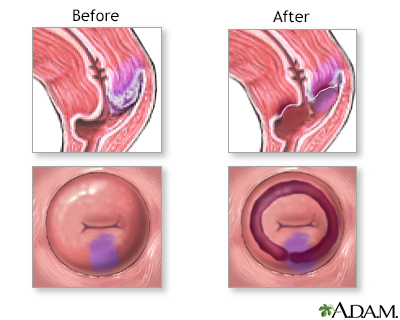
Cervical cancer is one of the most common cancers in women. It is a cancer of the epithelial tissue of the cervix. Pap smear is the screening procedure used to detect cervical cancer. Limited or early cervical cancer (carcinoma in situ, or cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, or dysplasia) requires treatment with ablation therapy, usually in the form of cervical cryotherapy, or a more extensive procedure, called conization, which removes more tissue.
|
|
| Procedure, part 1 |
|
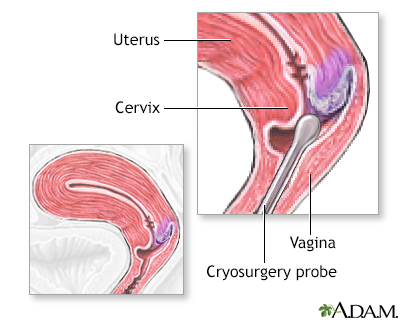
Ablation therapy is frequently performed using a cryoprobe. A hollow metal probe, through which flows extremely cold liquid nitrogen, is inserted into the vagina and applied to the cervix and held in place for 5 to 10 minutes. This freezes, and thus destroys, the superficial tissues of the cervix which contains the dysplastic tissue.
|
|
| Procedure, part 2 |
|
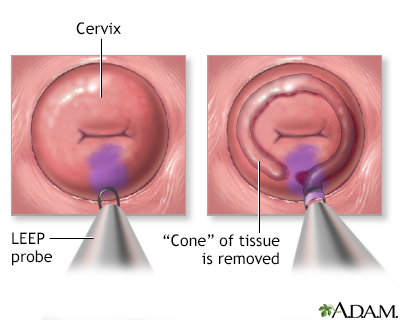
Conization is a procedure in which a "cone" of tissue is removed. This procedure is performed for more advanced cervical dysplasia, which remains limited to the cervix (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, high grade). It allows the surgeon to remove more cervical tissue.
Conization is performed using either a knife, laser, or electrocautery. LEEP, or the loop electrosurgical excision procedure is the term used for conization electrocautery. In this procedure, an electric current is run through a loop of wire, which is used to perform the conization. It is the most common method used for conization.
|
|
| Aftercare |
|
If the tissue removed by conization shows residual tumor, or invasive cancer, then further treatment is necessary. This often consists of surgical removal of the uterus and cervix (hysterectomy).
|
|

|
Review Date:
3/31/2024
Reviewed By:
LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
© 1997-

All rights reserved.