Omphalocele repair
| Normal anatomy |
|
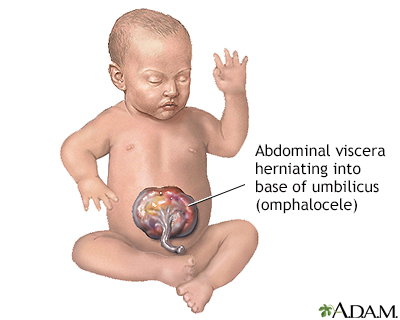
Omphalocele is an abdominal wall defect at the base of the umbilical cord (umbilicus); the infant is born with a sac protruding through the defect which contains small intestine, liver, and large intestine. Omphalocele is frequently associated with other birth defects, such as heart defects, imperforate anus, urinary problems, and genetic defects. Omphalocele is very similar to gastroschisis, except that the organs are enclosed in a sac.
|
|
| Indications |
|
Omphalocele is a life-threatening event requiring immediate intervention. The infant may be born underweight (small for gestational age) due to stress from this condition before birth.
|
|
| Procedure |
|
Immediately after delivery, the exposed organs are covered with warm, moist, sterile dressings. A tube is inserted into the stomach (nasogastric tube, also called NG tube) to keep the stomach empty to prevent choking on or breathing in (aspiration) stomach contents into the lungs. The surgery is done as soon as the infant is stable.
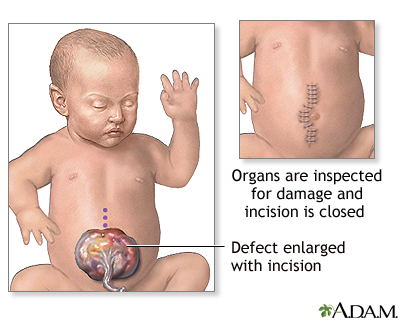
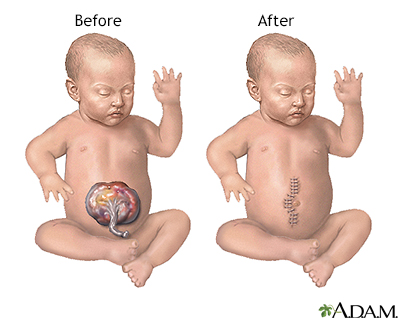
While the baby is deep asleep and pain-free (under general anesthesia) an incision is made to remove the sac membrane. The bowel is examined closely for signs of damage or additional birth defects. Damaged or defective portions are removed and the healthy edges stitched together. A tube is inserted into the stomach (gastrostomy tube) and out through the skin. The organs are replaced into the abdominal cavity and the incision closed, if possible.
|
|
| Aftercare |
|
The infant is cared for post-operatively in a neonatal intensive care unit. The baby is placed in an isolette (incubator) to keep warm and prevent infection. Oxygen is given and mechanical ventilation is often required. Intravenous fluids, antibiotics, and pain medications will be given. A nasogastric tube will be in place to keep the stomach emptied of gastric secretions. Feedings are started by nasogastric tube as soon as bowel function resumes. Feedings are started very slowly and often infants are reluctant to feed. These babies may need feeding therapy and lots of encouragement.
|
|

|
Review Date:
1/21/2025
Reviewed By:
Jonas DeMuro, MD, Diplomate of the American Board of Surgery with added Qualifications in Surgical Critical Care, Assistant Professor of Surgery, Renaissance School of Medicine, Stony Brook, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
© 1997-

All rights reserved.