Inguinal hernia repair
| Normal anatomy |
|
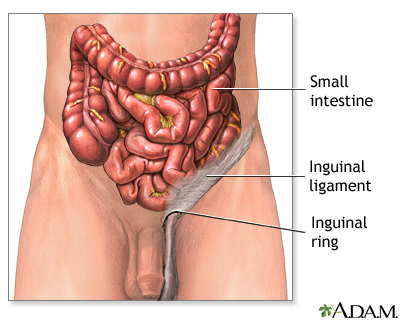
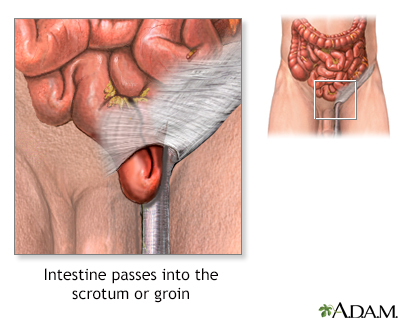
A hernia occurs when part of an organ protrudes through a weak point or tear in the thin muscular wall that holds the abdominal organs in place.
|
|
| Indications |
|
Hernia repair may be recommended for:
- Large bulges through a small hole (increased risk of incarceration and strangulation).
- Painful hernia. Inguinal hernia repair is indicated when the bulge through the inguinal canal is large or painful.
|
|
| Procedure |
|
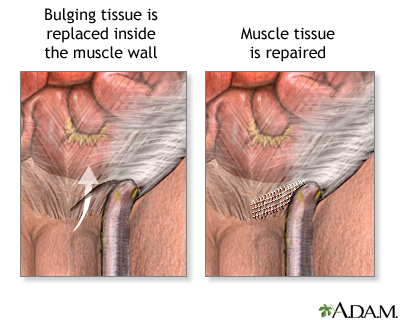
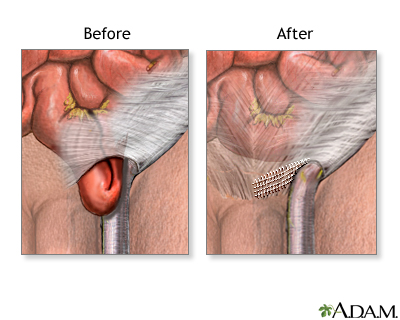
While the patient is sleepy (sedated) and pain-free (local anesthesia or spinal anesthesia) or deep asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia), an incision is made over the hernia. The bulging tissue or organ is replaced inside the muscle wall, the muscle tissue is repaired, and the skin is closed.
|
|
| Aftercare |
|
Moving and walking are recommended the day of surgery. Small children require no restrictions following routine hernia repair. Older children should avoid body contact sports for at least 3 weeks. The hernia repair is not at risk, but a blow to the incision could burst the skin closure. Expect complete recovery from surgery in about 2 to 4 weeks.
Avoid heavy lifting or straining for several weeks after surgery. Avoid tub baths for at least 5 days after the operation, because soaking will separate the skin tapes and the wound could break open. Sponge bathing for infants and showering for older children are permitted the day after surgery. The wound tapes should be carefully patted dry after showering.
|
|

|
Review Date:
1/21/2025
Reviewed By:
Jonas DeMuro, MD, Diplomate of the American Board of Surgery with added Qualifications in Surgical Critical Care, Assistant Professor of Surgery, Renaissance School of Medicine, Stony Brook, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
© 1997-

All rights reserved.