Paraquat poisoning
Definition
Paraquat (dipyridylium) is a highly toxic weed killer (herbicide). In the past, the United States encouraged Mexico to use it to destroy marijuana plants. Later, research showed this herbicide was dangerous to workers who applied it to the plants. This article discusses poisoning caused by breathing in or swallowing paraquat.
This article is for information only. DO NOT use it to treat or manage an actual poison exposure. If you or someone you are with has an exposure, call the local emergency number (such as 911), or the local poison control center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States.
Alternative Names
Paraquat lung; Dipyridylium poisoning
Poisonous Ingredient
Paraquat (a bipyridyl compound)
Where Found
Paraquat is found in certain commercial herbicides used for weed control. In the United States, it is classified as a restricted-use chemical, meaning that only licensed individuals can purchase and apply it.
Symptoms
Symptoms of paraquat poisoning include:
- Burns and pain in the throat
- Choking
- Coma (lack of responsiveness)
- Difficulty breathing
- Nosebleed
- Seizures
- Shock (extremely low blood pressure)
- Stomach pain
- Vomiting, including vomiting blood
Severe exposure can cause:
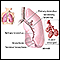
- Lung damage leading to pulmonary fibrosis (paraquat lung)
- Liver and kidney failure
- Damage to the esophagus and stomach
Before Calling Emergency
Have the following information ready:
- The person's age, weight, and condition
- The name of the product and ingredients (take the container if possible)
- The time and amount of exposure
Take the container with you to the hospital, if possible.
Poison Control
The local poison control center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States. This national hotline will let you talk to experts in poisoning. They will give you further instructions.
This is a free and confidential service. All local poison control centers in the United States use this national number. You should call if you have any questions about poisoning or poison prevention. It does NOT need to be an emergency. You can call for any reason, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
You can also get online poison help now at Poisonhelp.org. Just enter the product, poison, or medicine to get expert help.
What to Expect at the Emergency Room
Your health care provider will measure and monitor your vital signs, including temperature, pulse, breathing rate, and blood pressure. Tests that may be done include:
- Blood and urine tests
- Chest x-ray
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Bronchoscopy (tube through the mouth and throat) to view any lung damage
- Endoscopy (tube through the mouth and throat) to look for any damage to the esophagus and stomach
Treatment may include:
- Activated charcoal (if ingestion was recent)
- Breathing support (oxygen or mechanical ventilation)
- IV fluids
- Medicines to manage symptoms
- Hemoperfusion (blood filtration through charcoal) in severe cases
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome depends on the amount of paraquat absorbed. Ingestion of even a small amount can be fatal. People with mild exposure may recover fully, but those who swallow the poison often develop fatal organ damage.
Breathing in paraquat may cause lung damage. Long-term exposure to paraquat may cause scarring of the lungs called pulmonary fibrosis. This makes it hard to breathe.
Paraquat causes damage to the body when it touches the lining of the mouth, stomach, or intestines. Paraquat may also damage the kidneys, liver, and esophagus (the tube that food goes down from your mouth to your stomach).
If paraquat is swallowed, death can quickly occur. Death may occur from a hole in the esophagus, or from severe inflammation of the area that surrounds the major blood vessels and airways in the middle of the chest (mediastinum).
References
Kuschner WG, Blanc PD. Acute responses to toxic exposures. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 103.
Meehan TJ. Care of the poisoned patient. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 135.
Welker KL, Thompson TM. Pesticides. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 152.
|
Review Date:
7/1/2025 Reviewed By: Jesse Borke, MD, CPE, FAAEM, FACEP, Attending Physician at Kaiser Permanente, Orange County, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.