Rectal bleeding
Definition
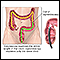
Rectal bleeding is when blood passes from the rectum or anus. Bleeding may be noted on the stool or be seen as blood on toilet paper or in the toilet. The blood may be bright red. The term "hematochezia" is used to describe this finding.
Alternative Names
Rectal bleeding; Blood in the stool; Hematochezia; Lower gastrointestinal bleeding; Melena
Considerations
The color of the blood in the stools may indicate the source of bleeding.
Black or tarry stools (melena) may be due to bleeding in the upper part of the GI (gastrointestinal) tract, such as the esophagus, stomach, or the first part of the small intestine. In this case, blood is most often darker because it gets digested on its way through the GI tract. Much less commonly, this type of bleeding can be brisk enough to present with bright red rectal bleeding.
Bleeding from the rectum may also be red or fresh. This usually means that the source of bleeding is the lower GI tract (colon, rectum, and anus).
Eating beets or foods with red food coloring can sometimes make stools appear reddish. In these cases, your health care provider can test the stool with a chemical to check for the presence of blood.
Causes
Rectal bleeding causes include:
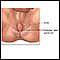
- Anal fissure (a cut or a tear in the anal lining, often caused by straining hard, hard stools or frequent diarrhea). It may cause sudden onset of rectal bleeding. There is most often pain at the anal opening.
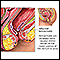
- Hemorrhoids, a common cause of bright red blood. They may or may not be painful.
- Proctitis (inflammation or swelling of the rectum and anus).
- Rectal prolapse (rectum protrudes from the anus).
- Trauma or foreign body.
- Colorectal polyps.
- Colon, rectal, or anal cancer.
- Ulcerative colitis and other types of colon inflammation (colitis)
- Infection in the intestines.
- Diverticulosis (abnormal pouches in the colon).
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if there is:
- Fresh blood in your stools
- Abdominal pain associated with blood or bloody mucus in the stool
- A change in the color of your stools
- Pain in the anal area while sitting or passing stools
- Incontinence or lack of control over passage of stools
- Unexplained weight loss
- Drop in blood pressure that causes dizziness or fainting
You should see your provider and have an exam, even if you think that hemorrhoids are causing the blood in your stool.
In children, a small amount of blood in the stool is most often not serious. The most common cause is constipation. You should still tell your child's provider if you notice this problem.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will take a medical history and perform a physical exam. The exam will focus on your abdomen and rectum.
You may be asked the following questions:
- Have you had any trauma to the abdomen or rectum?
- Have you had more than one episode of blood in your stool? Is every stool this way?
- Have you lost any weight recently?
- Is there blood on the toilet paper only?
- What color is the stool?
- When did the problem develop?
- What other symptoms are present (abdominal pain, vomiting blood, bloating, excessive gas, diarrhea, or fever?
You may need to have one or more exams or tests to look for the cause:
- Digital rectal exam.
- Anoscopy.
- Sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy to look inside your colon using a camera at the end of a thin tube to find or treat the source of bleeding may be needed.
- Angiography.
- Bleeding scan.
You may have one or more lab tests before, including:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Serum chemistries
- Clotting studies
- Stool culture or multiplex PCR test of stool to test for infection
References
DeGeorge LM, Nable JV. Gastrointestinal bleeding. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 26.
Kaplan GG, Ng SC. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and diagnosis of inflammatory bowel diseases. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 115.
Kovacs TO, Jensen DM. Gastrointestinal hemorrhage. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 121.
Kwaan MR. Hemorrhoids, anal fissure, and anorectal abscess and fistula. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, Heidelbaugh JJ, Lee EM, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2024. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:233-237
Savides TJ, Jensen DM. Gastrointestinal bleeding. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 20.
Swartz MH. The abdomen. In: Swartz MH, ed. Textbook of Physical Diagnosis: History and Examination. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 17.
|
Review Date:
6/11/2024 Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |