Dialysis - peritoneal
Definition
Dialysis treats end-stage kidney failure. It removes harmful substances from the blood when the kidneys cannot.
This article focuses on peritoneal dialysis.
Alternative Names
Artificial kidneys - peritoneal dialysis; Renal replacement therapy - peritoneal dialysis; End-stage renal disease - peritoneal dialysis; Kidney failure - peritoneal dialysis; Renal failure - peritoneal dialysis; Chronic kidney disease - peritoneal dialysis
Description
Your kidneys' main job is to remove toxins and extra fluid from your blood and regulate some aspects of your body's chemical balance. If waste products build up in your body, it can be dangerous and even cause death.
Kidney dialysis (peritoneal dialysis and other types of dialysis) does some of the job of the kidneys when they stop working well. This process:
- Removes extra salt, water, and waste products so they do not build up in your body
- Keeps safe levels of minerals and vitamins in your body
- Helps control blood pressure
- Helps produce red blood cells
WHAT IS PERITONEAL DIALYSIS?
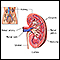
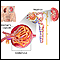
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) removes waste and extra fluid through the blood vessels that line the walls of your abdomen. A membrane called the peritoneum covers the walls of your abdomen.
PD involves putting a soft, hollow tube (catheter) into your abdominal cavity and filling it with a cleansing fluid (dialysis solution). The solution contains a type of sugar that draws out waste and extra fluid. The waste and fluid passes from your blood vessels through the peritoneum and into the solution. After a set amount of time, the solution and waste is drained and thrown away.
The process of filling and draining your abdomen is called an exchange. The length of time the cleansing fluid remains in your body is called the dwell time. The number of exchanges and the length of the dwell time depend on the method of PD you use and other factors.
Your doctor (kidney specialist or surgeon) will perform surgery to place the catheter in your abdomen where it will stay. It is most often near your belly button.
PD may be a good option if you want more independence and are able to learn to treat yourself. You will have a lot to learn and need to be responsible for your care. You and your caregivers must learn how to:
- Perform PD as prescribed
- Use the equipment
- Buy and keep track of supplies
- Prevent infection
With PD, it is important not to skip exchanges. Doing so can be dangerous to your health.
Some people feel more comfortable having a trained medical provider do some of their PD treatment. You and your health care provider (kidney specialist) can decide what is best for you.
TYPES OF PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
PD gives you more flexibility because you do not have to go to a dialysis center. You can have treatments:
- At home
- At work
- While traveling
There are 2 types of PD:
- Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). For this method, you fill your abdomen with fluid, then go about your daily routine until it is time to drain the fluid. You are not hooked up to anything during the dwell period, and you do not need a machine. You use gravity to drain the fluid. The dwell time is usually about 4 to 6 hours, and you will need 3 to 4 exchanges each day. You will have a longer dwell time at night while you sleep.
- Continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis (CCPD). With CCPD, you are connected to a machine that cycles through 3 to 5 exchanges at night while you sleep. You must be attached to the machine for 10 to 12 hours during this time. In the morning, you begin an exchange with a dwell time that lasts all day long. This allows you more time during the day without having to do exchanges.
The method you use depends on your:
- Preferences
- Lifestyle
- Medical condition
You can also use some combination of the two methods. Your provider will help you find the method that works best for you.
Your provider will monitor you to make sure the exchanges are removing enough waste products. You will also be tested to see how much sugar your body absorbs from the cleansing fluid. Depending on the results, you may need to make certain adjustments:
- To do more exchanges per day
- To use more cleansing fluid at each exchange
- To decrease the dwell time so you absorb less sugar
WHEN TO START DIALYSIS
Kidney failure is the last stage of long-term (chronic) kidney disease. This is when your kidneys can no longer support your body's needs. Your provider will discuss dialysis with you before you need it. In most cases, you will go on dialysis when you have only 10% to 15% of your kidney function left.
Risks
There is a risk for infection of the peritoneum (peritonitis) or the catheter site with PD. Your provider will show you how to clean and care for your catheter and prevent infection. Here are some tips:
- Wash your hands before performing an exchange or handling the catheter.
- Wear a surgical mask when performing an exchange.
- Look closely at each bag of solution to check for signs of contamination.
- Clean the catheter area with an antiseptic every day.
Watch the exit site for swelling, bleeding, or signs of infection. Contact your provider immediately if you have a fever or other signs of infection.
After the Procedure
Contact your provider right away if you notice:
- Signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, soreness, pain, warmth, or pus around the catheter
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Unusual color or cloudiness in used dialysis solution
- You are not able to pass gas or have a bowel movement
Also contact your provider if you experience any of the following symptoms severely, or they last more than 2 days:
- Itching
- Trouble sleeping
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Drowsiness, confusion, or problems concentrating
References
Bargman JM, Auguste BL. Peritoneal dialysis: principles, techniques, and adequacy. In: Johnson RJ, Floege J, Tonelli M, eds.Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 101.
Cohen D, Valeri AM. Treatment of irreversible renal failure. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 117.
Correa-Rotter R, Mehrota R, Saxena AB. Peritoneal dialysis. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 64.
|
Review Date:
10/28/2024 Reviewed By: Walead Latif, MD, Nephrologist and Clinical Associate Professor, Rutgers Medical School, Newark, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |