Adenoid removal
Definition
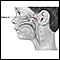
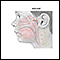
Adenoid removal is surgery to take out the adenoid glands. The adenoid glands sit behind your nose above the roof of your mouth in the nasopharynx. Air passes over these glands when you take a breath.
The adenoids are often taken out at the same time as the tonsils (tonsillectomy).
Adenoid removal is also called adenoidectomy. The procedure is most often done in children.
Alternative Names
Adenoidectomy; Removal of adenoid glands
Description
Your child will be given general anesthesia before surgery. This means your child will be asleep and unable to feel pain.
During surgery:
- The surgeon places a small tool into your child's mouth to keep it open.
- The surgeon removes the adenoid glands using a spoon-shaped tool (curette). Or, another tool that helps cut away soft tissue is used.
- Some surgeons use electricity to heat the tissue, remove it, and stop bleeding. This is called electrocautery. Another method uses radiofrequency (RF) energy to do the same thing. This is called coblation. A cutting tool called a microdebrider can also be used to remove the adenoid tissue.
- Absorbent material called packing material may also be used to control bleeding.
Your child will stay in the recovery room after surgery. You will be allowed to take your child home when your child is awake and can breathe easily, cough, and swallow. In most cases, this will be a few hours after surgery.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
A health care provider may recommend this procedure if:
- Enlarged adenoids are blocking your child's airway. Symptoms in your child can include heavy snoring, problems breathing through the nose, and episodes of not breathing during sleep.
- Your child has chronic ear infections that occur often, continue despite use of antibiotics, cause hearing loss, or cause your child to miss a lot of school days.
Adenoidectomy may also be recommended if your child has tonsillitis that keeps coming back.
The adenoids normally shrink as children grow older. Adults rarely need to have them removed.
Risks
Risks of any anesthesia are:
- Reactions to medicines
- Breathing problems
Risks of any surgery are:
- Bleeding
- Infection
Before the Procedure
Your provider will tell you how to prepare your child for this procedure.
A week before the surgery, do not give your child any medicine that thins the blood unless your surgeon says to do so. Such medicines include aspirin and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin).
The night before the surgery, your child should have nothing to eat or drink after midnight. This includes water.
You will be told what medicines your child should take on the day of surgery. Have your child take the medicine with a sip of water.
After the Procedure
Your child will go home on the same day as surgery. Complete recovery takes about 1 to 2 weeks.
Follow instructions on how to care for your child at home.
Outlook (Prognosis)
After this procedure, most children:
- Breathe better through the nose
- Have fewer and milder sore throats
- Have fewer ear infections
In rare cases, adenoid tissue may grow back. This does not cause problems most of the time. However, it can be removed again if necessary.
References
Schilder AGM, Rosenfeld RM, Venekamp RP. Acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 199.
Told TN. Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 66.
Zur KB. Tonsils and adenoids. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 431.
Reviewed By: Ashutosh Kacker, MD, FACS, Professor of Clinical Otolaryngology, Weill Cornell Medical College, and Attending Otolaryngologist, New York-Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.