Annular pancreas
Definition
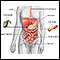
An annular pancreas is a ring of pancreatic tissue that encircles the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). The normal position of the pancreas is next to, but not surrounding the duodenum.
Causes
Annular pancreas is problem present at birth (congenital defect). Symptoms occur when the ring of pancreas squeezes and narrows the small intestine so that food cannot pass easily or at all.
Newborns may have symptoms of complete blockage of the intestine. However, up to one half of people with this condition do not have symptoms until adulthood. There are also cases that are not detected because the symptoms are mild.
Conditions that may be associated with annular pancreas include:
- Down syndrome
- Excess amniotic fluid during pregnancy (polyhydramnios)
- Other congenital gastrointestinal problems
- Pancreatitis
Symptoms
Newborns may not feed well. They may spit up more than normal, not drink enough breast milk or formula, and cry.
Adult symptoms may include:
- Abdominal pain
- Fullness after eating
- Nausea or vomiting
Exams and Tests
Tests include:
Treatment
Treatment most often involves surgery to bypass the blocked part of the duodenum.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome is most often good with surgery. Adults with an annular pancreas are at increased risk for pancreatic or biliary tract cancer.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Obstructive jaundice
- Pancreatic cancer
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
- Peptic ulcer
- Perforation (tearing a hole) of the intestine due to obstruction
- Peritonitis
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you or your child has any symptoms of annular pancreas.
References
Maqbool A, Bales C, Liacouras CA. Intestinal atresia, stenosis, and malrotation. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 356.
Mehta MS, Barth BA, Husain SZ. Anatomy, histology, embryology, and developmental anomalies of the pancreas. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 55.
Semrin MG. Anatomy, histology, and developmental anomalies of the stomach and duodenum. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 49.
|
Review Date:
12/31/2023 Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.