Cardiomyopathy
Definition
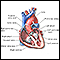
Cardiomyopathy is disease in which the heart muscle becomes weakened, stretched, or has another structural problem. It often contributes to the heart's inability to pump or function well.
Many people with cardiomyopathy have heart failure.
Causes
There are many types of cardiomyopathy, with different causes. Some of the more common causes are:
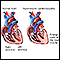
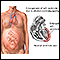
- Dilated cardiomyopathy (also called idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy if there is no known cause) is a condition in which the heart becomes weak and the heart's chambers get large. As a result, the heart cannot pump enough blood out to the body. It can be caused by many medical problems.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a condition in which the heart muscle becomes thick. This makes it harder for blood to leave the heart. This type of cardiomyopathy is most often passed down through families.
- Ischemic cardiomyopathy is caused by a narrowing of the arteries that supply the heart with blood. It makes the heart walls thin so they do not pump well.
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy is due to a group of disorders. The heart chambers are unable to fill with blood because the heart muscle is stiff. The most common causes of this type of cardiomyopathy are amyloidosis and scarring of the heart from an unknown cause.
- Peripartum cardiomyopathy occurs during pregnancy or in the first 5 months afterward.
Treatment
When possible, the cause of cardiomyopathy is treated. Medicines and lifestyle changes are often needed to treat the symptoms of heart failure, angina, and abnormal heart rhythms.
Procedures or surgeries may also be used, including:
- A defibrillator that sends an electrical pulse to stop life-threatening abnormal heart rhythms
- A pacemaker that treats a slow heart rate or helps the heart beat in a more coordinated fashion
- Coronary artery bypass (CABG) surgery or angioplasty that may improve blood flow to the damaged or weakened heart muscle
- Heart transplant that may be tried when all other treatments have failed
Partially and fully implantable mechanical heart pumps have been developed. These may be used for very severe cases. However, not all people need this advanced treatment.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook depends on many different things, including:
- Cause and type of cardiomyopathy
- The severity of the heart problem
- How long the problem has been present
- How well the condition responds to treatment
Heart failure is most often a long-term (chronic) illness. It may get worse over time. Some people develop severe heart failure. In this case, medicines, surgery, and other treatments may no longer help.
People with certain types of cardiomyopathy are at risk for dangerous heart rhythm problems.
References
Elliott PM, Olivotto I. Diseases of the myocardium and endocardium. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 47.
Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79(17):e263-e421. PMID: 35379503 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35379503/.
Hershberger RE. The dilated, restrictive, and infiltrative cardiomyopathies. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 52.
McMurray JJV, Pfeffer MA. Heart failure: treatment and prognosis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 46.
Rogers JG, O'Connor CM. Heart failure: epidemiology, pathobiology and diagnosis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 45.
Reviewed By: Thomas S. Metkus, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine and Surgery, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.