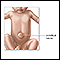
Umbilical hernia
Definition
An umbilical hernia is an outward bulge in the area around the belly button. It occurs when internal organs or the abdominal lining bulges through the muscles near the belly button.
Causes
In the womb, the umbilical cord is attached to the baby through an opening in the baby's abdomen. After birth, this opening normally closes. When this area doesn't close completely, it leaves a weak spot in the abdomen, which can lead to a hernia. Hernias may be seen after birth or later in life.
Umbilical hernias are common in infants. They occur slightly more often in African Americans. Most umbilical hernias are not related to disease. Some umbilical hernias are linked with rare conditions such as Down syndrome.
Symptoms
A hernia can vary in width from less than 1 centimeter (cm) to more than 5 cm (about 1/2 to 2 inches).
There is a soft swelling over the belly button that often bulges when the baby sits up, cries, or strains. The bulge may be flat when the infant lies on the back and is quiet. Umbilical hernias are usually painless.
Exams and Tests
A hernia is usually found by the health care provider during a physical exam.
Treatment
Most hernias in children heal on their own. Surgery to repair the hernia is needed only in the following cases:
- The hernia does not heal after the child is 3 or 4 years old.
- The intestine or other tissue bulges out and loses its blood supply (becomes strangulated). This is an emergency that needs surgery right away.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most umbilical hernias get better without treatment by the time the child is 3 to 4 years old. If surgery is needed, it is usually successful.
Possible Complications
Strangulation of the intestines can occur. This complication is rare but serious and needs surgery right away.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider or go to the emergency room if:
- Your baby is very fussy
- Your baby seems to have bad abdominal pain
- The hernia becomes tender, swollen, or discolored
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent an umbilical hernia. Taping or strapping an umbilical hernia will not make it go away.
References
Nathan AT. The umbilicus. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 125.
Sujka JA, Holcomb GW. Umbilical and other abdominal wall hernias. In: Holcomb GW, Murphy JP, St. Peter SD, eds. Holcomb and Ashcraft's Pediatric Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 49.
|
Review Date:
8/5/2023 Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.