| Dietary fats explained |
Fats are organic compounds that are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They are a source of energy in foods. Fats belong to a group of substances called lipids and come in liquid or solid form. All fats are combinations of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Fats can be called saturated or unsaturated depending on their proportions.
Fat is one of the three nutrients (along with protein and carbohydrates) that supply calories to the body. Fat provides 9 calories per gram, more than twice the number provided by carbohydrates or protein.
Fat is essential for the proper functioning of the body. Fats provide essential fatty acids, which are not made by the body and must be obtained from food. The essential fatty acids are linoleic and linolenic acid. They are important for controlling inflammation, blood clotting, and brain development.
Fat serves as the storage substance for the body's extra calories. It fills the fat cells (adipose tissue) that help insulate the body. Fats are also an important energy source. When the body has used up the calories from carbohydrate, which occurs after the first 20 minutes of exercise, it begins to depend on the calories from fat.
Healthy skin and hair are maintained by fat. Fat helps in the absorption, and transport through the bloodstream of the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K.
The types of fat
- Unsaturated fats: Fats that help to lower blood cholesterol if used in place of saturated fats. However, unsaturated fats have a lot of calories, so you still need to limit them. There are two types: mono-unsaturated and polyunsaturated. Most (but not all) liquid vegetable oils are unsaturated. (The exceptions include coconut, palm, and palm kernel oils.)
- Mono-unsaturated fats: Fats that help to lower blood cholesterol if used in place of saturated fats. However, mono-unsaturated fats have a lot of calories, so you still need to limit them. Examples include olive and canola oils.
- Polyunsaturated fats: Fats that help to lower blood cholesterol if used in place of saturated fats. However, polyunsaturated fats have a lot of calories, so you still need to limit them. Examples include safflower, sunflower, corn, and soybean oils.
- Trans fatty acids: These fats form when vegetable oil hardens (a process called hydrogenation) and can raise LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels. They can also lower HDL (“good”) cholesterol levels. Trans-fatty acids are found in fried foods, commercial baked goods (donuts, cookies, and crackers), processed foods, and margarines.
- Hydrogenated: refers to oils that have become hardened (such as hard butter and margarine). Foods made with hydrogenated oils should be avoided because they contain high levels of trans fatty acids, which are linked to heart disease. (Look at the ingredients in the food label.) The terms "hydrogenated" and "saturated" are related. An oil becomes saturated when hydrogen is added (i.e., becomes hydrogenated).
- Partially hydrogenated: Refers to oils that have become partially hardened. Foods made with partially hydrogenated oils should be avoided because they contain high levels of trans fatty acids, which are linked to heart disease. (Look at the ingredients in the food label.)
- Saturated fats: These are the biggest dietary cause of high LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels. When looking at a food label, avoid foods that have a percentage of saturated fat. Saturated fats should be limited to 10% of calories. Saturated fats are found in animal products such as butter, cheese, whole milk, ice cream, cream, and fatty meats. They are also found in some vegetable oils -- coconut, palm, and palm kernel oils. (Note: most other vegetable oils contain unsaturated fat and are healthy.)
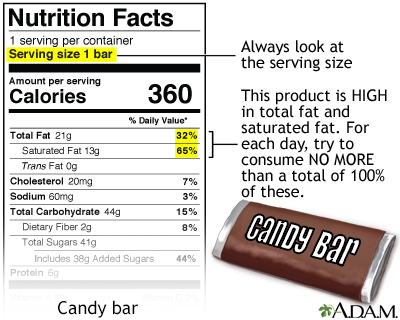
Eating too much saturated fat is one of the major risk factors for heart disease. A diet high in saturated fat causes a soft, waxy substance called cholesterol to build up in the arteries. Too much fat also increases the risk of heart disease because of its high calorie content, which increases the chance of becoming obese (another risk factor for heart disease and some types of cancer).

A large intake of polyunsaturated fat may increase the risk for some types of cancer. Reducing daily fat intake is not a guarantee against developing cancer or heart disease, but it does help reduce the risk.
Recommendations
- Choose lean, protein-rich foods -- soy, fish, skinless chicken, very lean meat, and fat free or 1% dairy products.
- Eat foods that are naturally low in fat -- like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Get plenty of soluble fiber -- with oats, bran, dry peas, beans, cereal, and rice.
- Limit your consumption of fried foods, processed foods, and commercially prepared baked goods (donuts, cookies, and crackers).
- Limit animal products like egg yolks, cheeses, whole milk, cream, ice cream, and fatty meats (and large portions of meats).
- Look at food labels, especially for the level of saturated fat. Avoid or limit foods high in saturated fat.
- Look on food labels for words like "hydrogenated" or "partially hydrogenated" -- these foods are loaded with bad fats and should be avoided.
- Liquid vegetable oil, soft margarine, and trans fatty acid-free margarine are preferable to butter, stick margarine, or shortening.
- Children under 2 years of age should NOT be on a fat restricted diet because cholesterol and fat are thought to be important nutrients for brain development.
It is important to read the nutrition labels and be aware of the amount of different types of fat contained in food. It is recommended that everyone over 20 have their cholesterol checked.
Talk to your health care provider about how to cut down your fat intake and to have your cholesterol checked.
|
Review Date:
6/28/2011 Reviewed By: Jeffrey Heit, MD, Internist with special emphasis on preventive health, fitness and nutrition, Philadelphia VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc. |
