| High blood pressure glossary |
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
|
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: Class of blood pressure medications that work by reducing the production of angiotensin, a chemical that causes arteries to constrict.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Alpha blockers: Class of blood pressure medications blocking sympathetic adrenergic innervation that causes arteries to constrict.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Beta blockers: Class of blood pressure medications that ease the heart's pumping action and heart rate reducing the stress on blood vessels. They competitively inhibit adrenaline.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Angiotensin-receptor blockers: Class of blood pressure medications that block the effects of angiotensin, a chemical that causes arteries to constrict. Works much like ACE inhibitors but tends to have fewer side effects.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Angiotensin-renin-aldosterone system: Group of hormones that are believed to play a major role in blood pressure control.
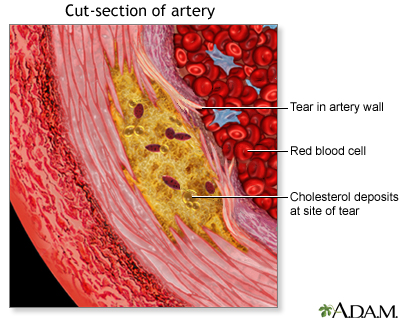
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Atherosclerosis: A slow, complex disease in which sticky deposits (called plaque) build up in the inner lining of an artery. Atherosclerosis can lead to heart disease or stroke.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Blood clot: A mass of congealed blood. Blood clots can block blood vessels and cause a stroke or heart attack.
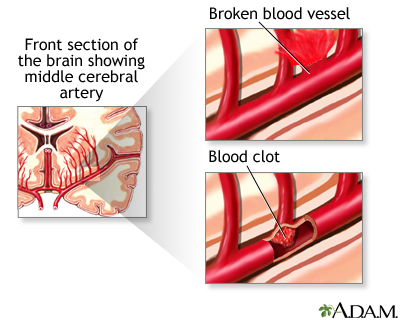
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Blood pressure: A measure of how hard blood is pressing against artery walls. Blood pressure is recorded as two numbers: the top number is called systolic pressure and the bottom number is called diastolic pressure.
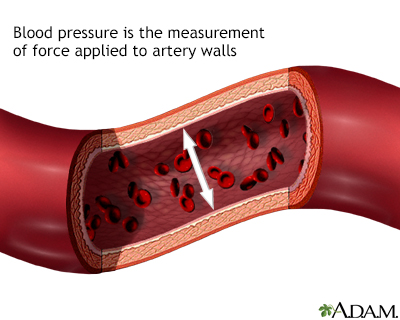
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Blood test: A test that involves withdrawing a sample of blood from your arm for examination. Blood tests are used to detect organ damage and diseases caused by high blood pressure.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Calcium channel blockers: Class of blood pressure medications that relax and widen the blood vessels.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Cardiovascular disease: Any disease that affects the circulatory system -- this includes the heart and blood vessels.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Cholesterol: A soft waxy substance that is a natural component of the fats in the bloodstream and is used by all the cells of the body. There is a "good" form of cholesterol (HDL), which protects the heart, and a "bad" form (LDL), which causes heart disease and other problems.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Corticosteroids: A group of steroid drugs similar to the natural corticosteroid hormones produced by the body. When taken by mouth or injected into the skin, corticosteroids can raise blood pressure.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Cushing's disease: A complex disease caused by an excess of cortisol (a steroid-like hormone produced by the body). High cortisol levels can raise blood pressure.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet: A balanced, healthful diet that is low in salt and rich in fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products. The DASH diet is very effective for people with high blood pressure.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Diabetes: A chronic disease associated with abnormally high levels of sugar in the blood. People with diabetes are at risk for developing high blood pressure.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Diastolic pressure: Pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest. It is the bottom number of a blood pressure reading.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Diuretics: Class of blood pressure medications that cause the body to excrete water and sodium (salt).
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Electrocardiogram (ECG): A recording of the electrical activity of the heart. ECGs are used to detect heart damage that may be caused by high blood pressure.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Essential hypertension: Type of high blood pressure in which there is no specific cause. Nine out of 10 people with high blood pressure have essential hypertension.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
HDL cholesterol: Good cholesterol. Removes LDL ("bad") cholesterol from artery walls and protects against heart disease.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Heart attack: Complete blockage of blood flow to an area of the heart. This causes some heart muscle to die and creates scar tissue. If not treated properly, high blood pressure can lead to a heart attack.
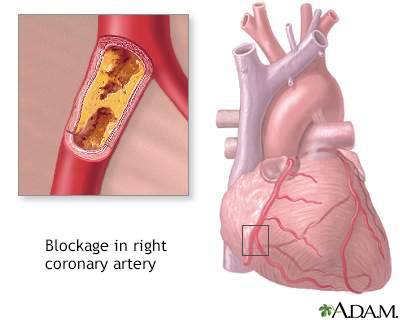
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Heart disease: A condition in which sticky deposits (called plaque) block the flow of blood to the heart. Heart disease is also called coronary artery disease. If not treated properly, high blood pressure can lead to heart disease.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
High blood pressure: When blood pushes against artery walls harder than normal, all or most of the time. High blood pressure puts a strain on blood vessels throughout your body and increases the workload on the heart. This can lead to organ damage. It often has no obvious cause, although many factors can contribute.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
High cholesterol: Too much cholesterol circulating in the blood. This can create sticky deposits (called plaque) along the artery walls and may lead to heart disease and atherosclerosis.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Hypertension: High blood pressure.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Isolated systolic hypertension (ISH): A type of high blood pressure in which only the systolic blood pressure is too high.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
LDL cholesterol: Bad cholesterol. If it deposits in the walls of blood vessels, it can lead to atherosclerosis and heart disease.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): A government organization that conducts research and provides public information about diseases of the heart, lungs, and blood.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Nitric oxide (NO): A molecular gas produced by the body that helps keep blood vessels relaxed and flexible. Low levels of NO may contribute to high blood pressure.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Nondipper hypertension: Condition in which blood pressure does not fall during sleep as it should.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Medications commonly prescribed or purchased over the counter to reduce inflammation. Examples include aspirin and ibuprofen. Using NSAIDs for long periods of time can raise blood pressure.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Plaque: Sticky deposits that build up in the inner lining of an artery. A build-up of plaque in the arteries can lead to heart disease and stroke. Plaque is another name for atherosclerosis.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Potassium: Potassium is an essential mineral that helps the kidneys function normally. It also plays a key role in cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle contraction, making it an important nutrient for normal heart, digestive, and muscular function.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Preeclampsia: Severe and sudden rise in blood pressure that occurs in some women during the late second and third trimester of pregnancy. Women with preeclampsia also experience swelling of the arms, hands, and face.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
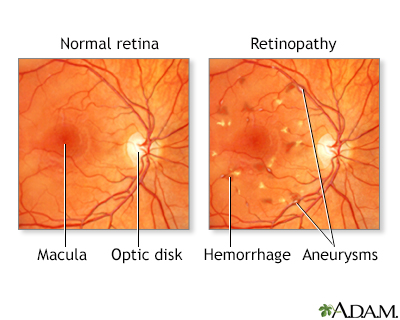
Retinopathy: Degenerative disease of the retina (light-sensitive portion of the eye). Retinopathy can be caused or worsened by high blood pressure.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Secondary hypertension: Type of high blood pressure in which the specific cause is known. Causes of secondary hypertension include kidney disease, certain medications, and heavy alcohol use.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Sleep apnea: Disorder in which breathing halts briefly but repeatedly during sleep. Sleep apnea can cause high blood pressure.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Sodium: Salt
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Sphygmomanometer: Blood pressure cuff. This instrument is used to measure systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Stethoscope: An instrument used to hear sounds made by the heart, lungs, and other organs.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Stroke: Death of brain cells caused by obstructed blood flow to parts of the brain. If not treated properly, high blood pressure can cause a stroke.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Systolic pressure: Pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts or beats. It is the top number of a blood pressure reading.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Urinalysis: Urine test. This test is used to detect kidney damage associated with high blood pressure.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Vasodilators: Class of blood pressure medications that work by expanding blood vessels.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
White coat hypertension: A condition in which blood pressure rises in the presence of a doctor or nurse, but returns to normal when not in the doctor's office.
Reviewed By: Steven Kang, MD, Division of Cardiac Pacing and Electrophysiology, East Bay Arrhythmia, Cardiovascular Consultants Medical Group, Oakland, CA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.

