| Step 10: Avoid long-term complications |
Learn to keep track of the ABCs of diabetes -- A1C, blood pressure, and cholesterol. Keeping these three in the healthy range can go a long way toward preventing long-term complications. For many people, the goal is to have an A1C of less than 7%, blood pressure of less than 130/80, and LDL cholesterol of less than 100. However, these goals are often individualized, and you should check with your health care team to see what is best for you. For example, people with heart disease may have a higher A1C goal in order to avoid low blood sugar. Your A1C should at least 2 - 4 times a year (as long as it is at or near your goal). Know your latest numbers. If your A1C is greater than 7%, your blood pressure is over 130/80, or your LDL cholesterol is above 100, it may be time to take action.
Over time, poorly controlled diabetes can lead to a variety of serious health conditions, including heart disease, stroke, blindness, amputations, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regular checkups are important throughout the life of a person with diabetes.
Heart disease and stroke
Over a period of years, diabetes can have a big impact on your heart and blood vessels. The problem needs to be taken seriously -- people with diabetes are at high risk of heart attack, stroke, and heart failure. According to the American Diabetes Association, these problems can occur at a younger age than they do in people without diabetes, and they are more deadly. In fact, heart disease and related complications are the leading cause of death in people with diabetes.
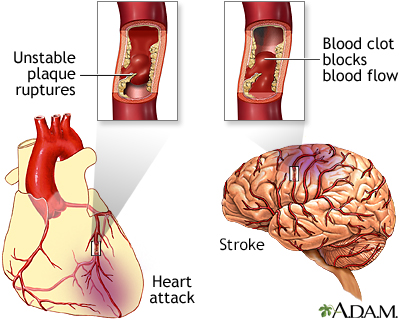
| A heart attack or stroke may occur when an area of plaque (atherosclerosis) ruptures and a clot forms over the location, blocking the flow of blood to the organ's tissues. |
You can take steps to minimize the risks:
|
There are many ways to keep your heart healthy and reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems down the road. Talk to your doctor to learn what may benefit your situation.
Nerve damage (neuropathy)
Diabetes can damage the nerves and cause a complication called neuropathy. This generally begins as loss of sensation in your toes, and possibly fingers. Eventually, the neuropathy can move up your legs or arms. Symptoms to watch out for include:
- Tingling
- Weakness
- Burning sensations
- Loss of sensitivity to warmth or cold
- Numbness -- if the nerves are damaged enough, you may be unaware that a blister or minor wound has become infected.
- Abnormal drop in blood pressure when you stand up
- Problems with bowel and bladder control
- Impotence in men
- Bone deformity in foot ("Charcot foot")
You may even have a heart attack and not be able to feel any chest pain.
Poor circulation
If you have diabetes, you are at risk for blood vessel injury, which may be severe enough to cause tissue damage in your legs and feet. If nerve damage is also a problem, then you may not be aware of the injuries that have occurred in your legs or feet.
At that point, minor infections sometimes develop into deep tissue injuries that may even require surgery. In extreme cases, amputation of the foot or limb may be necessary. Good foot care is very important to prevent problems.

- Check your feet every day.
- If you have any questions about foot care -- calluses, sores, how to trim nails, which shoes to wear -- call your doctor or diabetes educator.
- Report any problems (like loss of sensation or sign of infection) to your doctor right away.
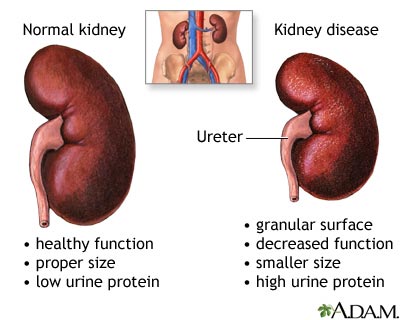
Kidney disease
The kidneys filter and clean blood. Not surprisingly, having too much glucose in the blood puts a strain on them. Over time, this can actually lead to kidney failure. When this happens, dialysis or a kidney transplant may be needed.
|
Eye problems
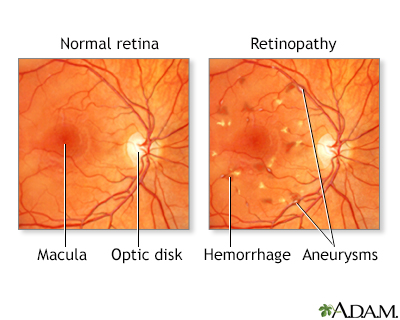
Diabetes is the leading cause of blindness in adults. The most common eye disorder in diabetes is retinopathy. This condition is caused by the excessive amount of glucose in the bloodstream, which weakens and damages the blood vessels. A weakened blood vessel may bulge out (aneurysm). Sometimes extra blood vessels appear and may even rupture, leaking blood and fluid into the surrounding tissues (hemorrhage). Either of these can cause vision problems. Diabetes puts you at higher risk for developing cataracts and certain types of glaucoma.
|
Other possible complications
- Gum disease
- Respiratory infections
- Urinary tract infections
Reviewed By: Nancy J. Rennert, MD, Chief of Endocrinology & Diabetes, Norwalk Hospital, Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Previoulsy reviewed by Ari S. Eckman, MD, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. (5/13/2010)
