| Step 8: Monitor blood glucose |
- Insulin
- Meal plan
- Blood glucose monitoring
- Exercise
Testing blood glucose is the only way to be sure that it is within normal range and allows you to adjust the insulin and eating plan if it is not. From day to day, it helps prevent emergencies. Over a period of years, it helps prevent or slow down long-term, serious complications of diabetes.
Follow your doctor's instructions for testing blood glucose every day -- even when symptoms are not present.
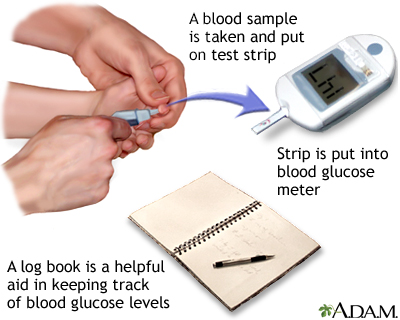
How to do it
The current method for monitoring blood glucose requires a finger-stick blood sample. Many people are squeamish about this at first, but most people quickly become comfortable with it. So don't worry -- you will, too!
The equipment you need to perform the finger-stick test includes a lancet (small blade or needle device for drawing blood from the finger), a blood glucose meter, test strips, and a log book. Your doctor can help you choose the appropriate equipment.
Make sure your hands are washed. (Or, if you are testing your child's blood, wash their hands.) Use a lancet to get a drop of blood from the SIDE of a finger. The tip of the finger is more sensitive and should not be used. Place the blood drop onto one of the special test strips. Insert the strip into the blood glucose meter. The meter analyses the amount of glucose in the blood sample.
Keep a log book handy, and write down the glucose level, time, and date each time you test. Bring this log book with you when you visit the doctor. Some meters keep a log automatically. You may be able to download the log to a computer or smart phone.
Your doctor will let you know how often you should check your blood sugar. This will depend on the number of injections and types of insulin you use. Many people with diabetes check their glucose reading at least 4 times a day, before meals and at bedtime. Most people aim for a range between 80 - 120 before meals and 100 - 140 at bedtime. It will go up and down over the course of the day. Ask your doctor what the best time is for you to test, and what your levels should be during different times of day.
Follow your meter's instructions for cleaning and calibration. This will help ensure accurate readings. Write the expiration date on your vial of test strips.
Hemoglobin A1c test
Another test to see how well blood sugar is under control is the hemoglobin A1c test. It measures blood sugar control over the last 3 months. This is a simple blood test usually done at the doctor's office. A home test is also available.
If you haven't had an A1c test in the past 3 - 4 months, call your doctor to request one.
 |
|
Reviewed By: Nancy J. Rennert, MD, FACE, FACP, Chief of Endocrinology & Diabetes, Norwalk Hospital, Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
