| Step 2: What is diabetes? |
Diabetes is a serious medical condition characterized by high levels of glucose in the blood.
Glucose is a simple sugar that comes from the food you eat. When your stomach digests food, glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream. The glucose circulates in your blood and serves as the main source of fuel for all the cells in your body.
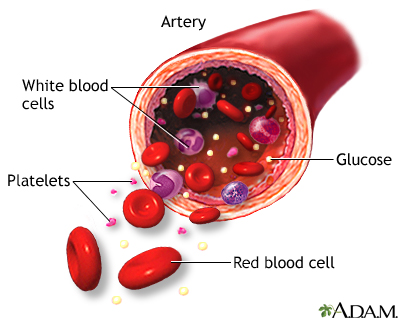
| All cells in the body need a continuous supply of energy to carry out normal body functions. Glucose, a simple sugar derived from the foods we eat, is the primary source of cellular energy. Glucose is transported throughout the body by the bloodstream. |
However, glucose cannot get inside cells by itself. Glucose needs insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, to transport it from blood into cells.
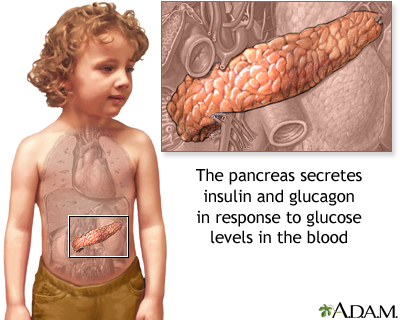
| The pancreas is a gland that lies behind the liver and stomach. |
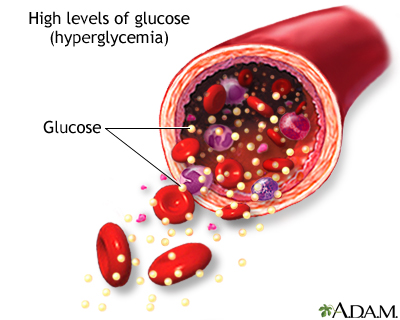
Diabetes occurs when the pancreas either can't produce any insulin at all or can't produce enough insulin to properly control blood sugar levels. When this happens, glucose builds up in the blood. This is a condition known as hyperglycemia. The result is that the body lacks the fuel it needs.
- Type 1 diabetes -- Usually starts in childhood, but it can occur at any age and accounts for 5 - 10% of all diagnosed cases of diabetes. People with type 1 diabetes produce little or no insulin and therefore must use insulin daily to control their blood sugars.
- Type 2 diabetes -- Usually starts in adulthood, although it is being diagnosed more often in children because of rising rates of childhood obesity. The symptoms can be subtle. Many people may not know they have type 2 diabetes. It is much more common than type 1, accounting for 90 - 95% of cases. People with type 2 diabetes initially are resistant to the insulin the body makes, and their pancreas may try to compensate by making more insulin. Over time (usually more than 10 - 15 years), the pancreas loses the ability to make excess insulin and may be make little or no insulin. Type 2 diabetes may be controlled with diet and exercise alone, but often patients need oral or injectable drugs or insulin.
- Gestational diabetes -- Some women develop this form of diabetes when they are pregnant. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after the baby is born, but the woman is then at very high risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in her life, and during another pregnancy.
- Sometimes, Type 1 diabetes is diagnosed in adults and can be mistaken as Type 2 diabetes. This is also referred to as latent autommune diabetes in adults (LADA).
 |
|
References
American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes--2009. Diabetes Care. 2009 Jan;32 Suppl 1:S13-61.
Reviewed By: Nancy J. Rennert, MD, FACE, FACP, Chief of Endocrinology & Diabetes, Norwalk Hospital, Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
