| Cholesterol glossary |
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
|
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Alzheimer's disease: A slowly progressing form of mental impairment, also known as senile dementia, usually occurring later in life. High cholesterol has been shown to be a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Angina: A pain in the chest caused by inadequate blood flow through the blood vessels of the heart.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Antioxidants: A vitamin or nutrient that may help prevent damage to the heart, arteries, and other tissues. Examples include vitamins C and E, and beta-carotene. (The American Heart Association believes data is currently inconclusive about the benefits of antioxidants on heart health.)
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Apolipoprotein B: This is the major protein component in LDL (low density lipoprotein). LDL, which is commonly called "LDL cholesterol" for simplicity, is actually a complex mixture of cholesterol and protein, including apolipoprotein B. The role of apolipoprotein B as part of the LDL molecule is to help transport cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. Apolipoprotein B may be an even better predictor of heart disease than LDL itself, although at this time it is not a major part of cholesterol screening. It may also be a future target for treatment.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
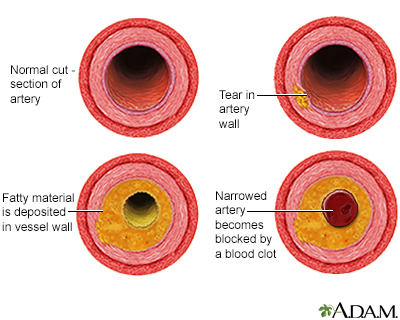
Arteriosclerosis: A disease characterized by building up of plaque or thickening and hardening of artery walls. The word "atherosclerosis" is often used to indicate any of the forms of arteriosclerosis.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Atherosclerosis: A slow, complex disease in which fatty deposits (called plaque) build up in the inner lining of an artery, eventually causing it to narrow and restrict blood flow. It is one of several types of "arterio"-sclerosis.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Beta blockers: A class of blood pressure medications that ease the heart's pumping action, widen the blood vessels, and lower heart rate and blood pressure. Beta blockers may interfere with bile acid resins.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Bile acid resins: A class of medications that lowers the amount of LDL ("bad") cholesterol in the blood. The body converts cholesterol to bile acid. The way the resin works is that it binds the bile acids, causing the bile acids to be removed in the intestines. In response, more LDL cholesterol is converted to bile acid, effectively removing it from the blood.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
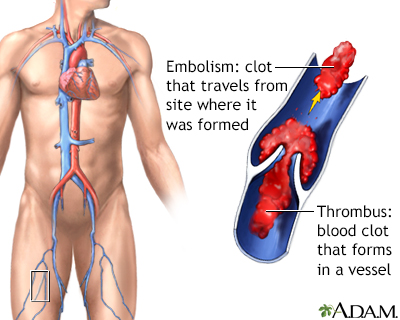
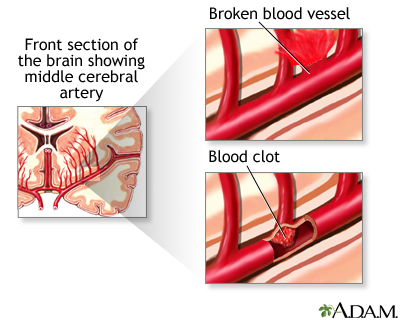
Blood clot: A mass of congealed blood. Blood clots can block blood vessels and cause a stroke or heart attack.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
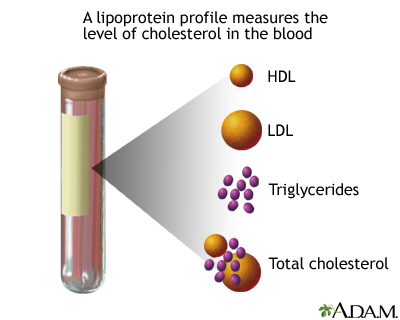
Blood test: A test that involves withdrawing a sample of blood from your arm for examination. A blood test known as a "lipid profile" is used to detect levels of cholesterol and triglycerides.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Cardiovascular disease: Any disease that affects the circulatory system -- this includes the heart and blood vessels.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
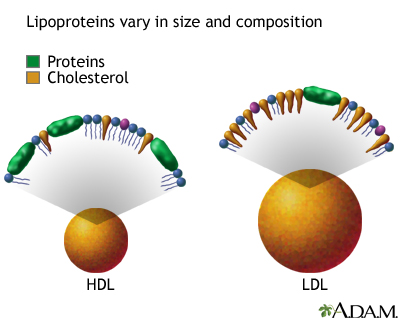
Cholesterol: A soft waxy substance that is a natural component of the fats in the bloodstream and is used by all the cells of the body. There is a "good" form of cholesterol (HDL), which protects the heart, and a "bad" form (LDL), which causes heart disease and other problems.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
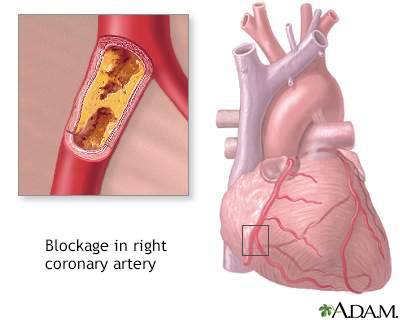
Coronary artery disease (CAD): Heart disuse. A condition in which sticky deposits (plaques) block the flow of blood to the heart, often causing chest pain (angina). Heart disease can lead to a heart attack. Untreated, high LDL cholesterol levels can lead to heart disease.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
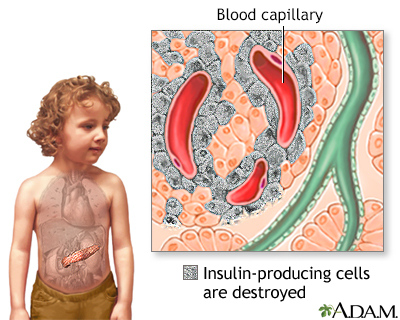
Diabetes: A chronic disease associated with abnormally high levels of sugar in the blood. People with diabetes should avoid using nicotinic acid.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Dyslipidemia: The medical term for an unhealthy blood lipid (fat) profile.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Fibrates: A class of lipid lowering medications that is used primarily to lower triglycerides and, to a lesser extent, LDL ("bad") cholesterol.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Gout: A condition in which too much uric acid in the body causes joint pains. People with gout should avoid using nicotinic acid.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
HDL cholesterol: Good cholesterol. Removes cholesterol from artery walls and protects against heart disease. You want your HDL level to be HIGH.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
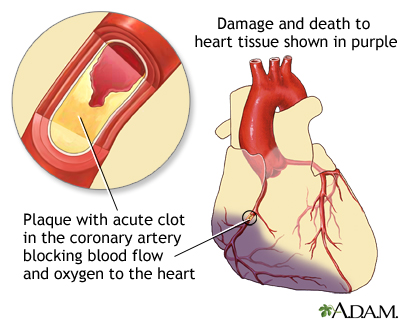
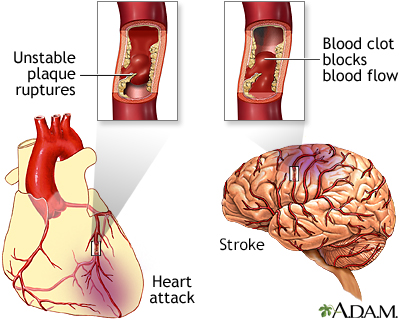
Heart attack: Also called a myocardial infarction. This is a complete blockage of blood flow to an area of the heart, causing heart cells to die. Untreated, high LDL cholesterol levels can lead to a heart attack.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Heart disease: Also called coronary artery disease. A condition in which sticky deposits (called plaque) block the flow of blood to the heart, often causing chest pain (angina). Heart disease can lead to a heart attack. Untreated, high LDL cholesterol levels can lead to heart disease.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
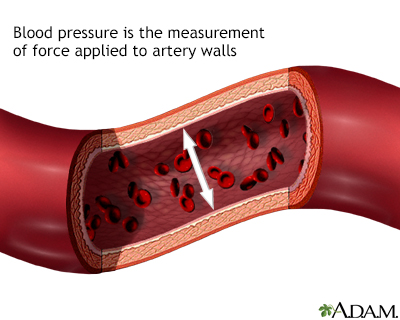
High blood pressure: When blood pushes against artery walls harder than normal, all or most of the time. This tends to happen when the arteries become too stiff or narrow.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
High cholesterol: An unhealthy level of LDL cholesterol circulating in the blood. (Note: when "total cholesterol" is high, it is a rough approximation that LDL is high.) High LDL cholesterol levels can create sticky deposits (called plaque) along the artery walls and may lead to heart disease and atherosclerosis.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Homocysteine: An amino acid that is found in the body. When levels of homocysteine are too high, it can be a risk factor for heart disease, even in people with normal cholesterol.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Hydrogenated: refers to oils that have become hardened (such as hard butter and margarine). Foods made with hydrogenated oils should be avoided because they contain high levels of trans fatty acids, which are linked to heart disease. (Look at the ingredients in the food label.) The terms "hydrogenated" and "saturated" are related; an oil becomes saturated when hydrogen is added (i.e., becomes hydrogenated).
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Hyperlipidemia: Medical term for high blood cholesterol.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Hypoglycemia: A condition in which the amount of sugar in the blood is abnormally low. Certain drugs taken to regulate blood sugar may react with bile acid resins.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
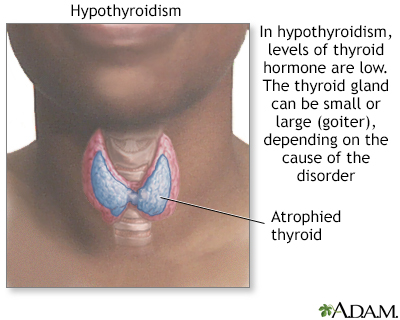
Hypothyroidism: A condition in which not enough thyroid hormone is produced. Hypothyroidism is a risk factor for high cholesterol.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
LDL cholesterol: Bad cholesterol. It deposits on the walls of blood vessels, and can lead to atherosclerosis and heart disease. You want your LDL level to be LOW.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
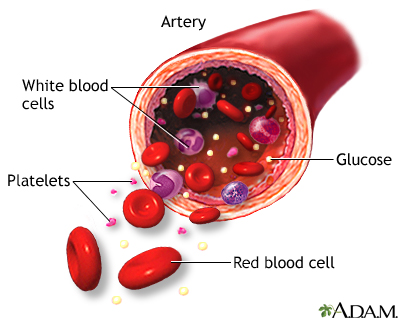
Lumen: The interior space of an artery though which the blood flows.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Mono-unsaturated fats: Fats that help to lower blood cholesterol if used in place of saturated fats. However, mono-unsaturated fats have a lot of calories, so you still need to limit them. Examples include olive and canola oils.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): A government organization that conducts research and provides public information about diseases of the heart, lungs, and blood.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Nicotinic acid (niacin): A form of vitamin B that raises the amount of HDL ("good") cholesterol in the blood.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Partially hydrogenated: Refers to oils that have become partially hardened. Foods made with partially hydrogenated oils should be avoided because they contain high levels of trans fatty acids, which are linked to heart disease. (Look at the ingredients in the food label.)
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Plaque: Sticky deposits that build up in the inner lining of an artery. Plaque buildup is called atherosclerosis and it can lead to heart disease and stroke.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Polyunsaturated fats: Fats that help to lower blood cholesterol if used in place of saturated fats. However, polyunsaturated fats have a lot of calories, so you still need to limit them. Examples include safflower, sunflower, corn, and soybean oils.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Psyllium: A soluble fiber supplement that is sometimes used with bile acid resins.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Rhabdomyolysis: A very rare condition of muscle deterioration that can lead to kidney failure. Rhabdomyolysis has been associated with certain statin drugs, particularly cerivastatin (Baycol) in high doses. (Baycol was withdrawn from the market.) Rhabdomyolysis is characterized by muscle aches and pains, as well as high blood levels of an enzyme called creatine kinase (CK) and creatinine (usually causing brown urine).
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Saturated fats: These are the biggest dietary cause of high LDL cholesterol levels. When looking at a food label, pay very close attention to the % of saturated fat and avoid or limit any foods that are high (for example, over 20% saturated fat). Saturated fats are found in animal products such as butter, cheese, whole milk, ice cream, cream, and fatty meats. They are also found in some vegetable oils -- coconut, palm, and palm kernel oils. (Note: most other vegetable oils contain unsaturated fat and are healthy.)
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Stroke: Death of brain cells caused by obstructed blood flow to parts of the brain. If not treated properly, high LDL cholesterol can cause a stroke.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Statins: A class of drugs used to lower LDL ("bad") cholesterol and triglycerides by inhibiting the body's production of them.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Trans fatty acids: These fats form when vegetable oil hardens (a process called hydrogenation) and can raise total cholesterol levels.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Triglyceride: A type of fat that is normally present in the blood. High levels of triglycerides are linked to heart disease and atherosclerosis.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Unsaturated fats: Fats that help to lower blood cholesterol if used in place of saturated fats. However, unsaturated fats have a lot of calories, so you still need to limit them. There are two types: mono-unsaturated and polyunsaturated. Most (but not all!) liquid vegetable oils are unsaturated. (The exceptions include coconut, palm, and palm kernel oils.)
Reviewed By: Norma Keller, MD, Assistant Professor, Cardiac and Vascular Institute, NYU Langone Medical Center, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Previously reviewed by Larry A. Weinrauch, MD, Asst. Prof. of Med., Harvard Medical School, and Private practice specializing in Cardiovascular Disease, Watertown, MA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network (10/10/2008).

