| Bloodless medicine glossary |
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
|
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Albumin: This major protein constituent of blood is often given to individuals who need to retain more fluid in their bloodstream, such as burn victims or patients with liver failure or extremely heavy bleeding (hemorrhage). Albumin (along with clotting factors, growth factors, and immunoglobulins) is sometimes referred to as a minor blood fraction. If you are a Jehovah's Witness, whether or not you can accept treatment with a minor blood fraction may be considered an individual "matter of conscience."
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Allogeneic blood: Blood donated from another individual, which is typically stored and then provided through a transfusion. Jehovah's Witnesses do not accept allogenic blood.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Anemia: A condition in which an individual's blood can't supply an appropriate amount of oxygen to their organs and tissues, either due to a low volume of blood, too few red blood cells in the blood, or too little hemoglobin or iron in the red blood cells. Patients who are suffering from severe anemia are sometimes more difficult to manage, unless they are treated by a team that is very experienced in transfusion-free medicine.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Apheresis: A process used to obtain blood components (such as platelets) from a donor. The blood is removed from the donor, the necessary cells are harvested and retained, and the donor's plasma is returned to the donor. Donated platelets are considered a major blood fraction and are not acceptable to Jehovah's Witnesses. However, "therapeutic apheresis" may be acceptable to some Jehovah's Witnesses because it is a treatment performed on the patient's own blood.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Blood banking: This is when blood is donated by a person for their own use or a specific individual's use at a later time. It is usually done because of fear that donor blood will not be available or might have contaminants, or because the person has a rare blood type. This procedure is not "bloodless medicine" because it involves blood storage and blood transfusions.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Blood salvage: Blood salvage procedures collect blood lost during or after surgery. A variety of methods may be used to collect blood, including suction and drainage devices. The devices that are used are sometimes called "cell savers." Those who object to blood transfusions may feel comfortable with "closed loop" blood salvage, where the blood is never stored and retains a semblance of connection to the patient at all times.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Cautery: Deliberate surgical destruction of tissue, either because the tissue is abnormal or to seal off a bleeding area. Cautery is a method of reducing bleeding during transfusion-free surgery. It may be achieved through heat, freezing, chemical scarring, electricity, light, and ultrasonic or microwave energy.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Cell savers: Devices that capture and hold blood during or after surgery, so that the blood can be returned to the patient.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
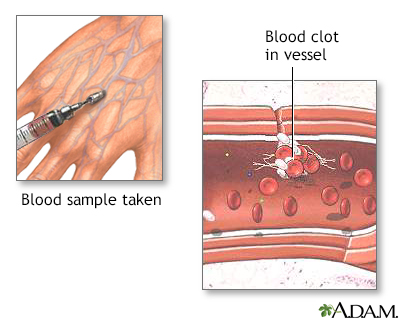
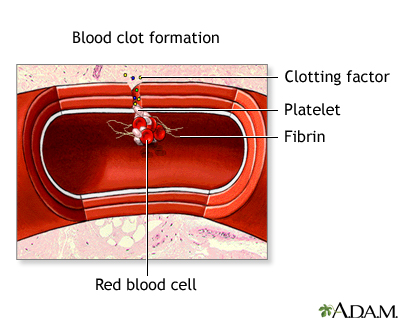
Clotting: The complex chain of chemical events that produces a plug (clot) at the site of bleeding. It is important for a patient undergoing transfusion-free surgery to have good clotting ability, in order to reduce bleeding/blood loss. Certain medications may interfere with clotting, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; anticoagulants (such as Coumadin); vitamin E; and herbal preparations containing garlic or ginkgo biloba.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Clotting factors: Chemicals that circulate in the blood and interact together to help cause blood clotting at the site of an injury.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Coagulation: The conversion of liquid (blood) into a somewhat solid plug that can prevent further bleeding from a particular site.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Colloidal solutions: Intravenous fluid solutions that contain water, salts, sugars, and protein. They may be given to replace the fluids, salts, and sugars that you will invariably lose during the course of surgery. Some colloidal solutions contain albumin -- a protein whose use is a matter of personal conscience for Jehovah's Witnesses.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Cryosurgery: A surgical technique that uses extreme cold to destroy abnormal tissues in the body. It is sometimes used as a bloodless medicine technique -- by freezing tissue, bleeding is minimized.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Crystalloid solutions: Intravenous fluid solutions that contain water, salts, and sugars. They may be given to replace the fluids, salts, and sugars that you will invariably lose during the course of surgery. Jehovah's Witnesses find cystalloid solutions such as Ringer's lactate and normal and hypertonic saline acceptable therapy.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Donor: A person who gives blood. The donated blood may be stored and distributed to hospitals and medical centers to be given to a patient when needed (as a transfusion). When a patient receives whole blood in this way, this is considered traditional medicine -- NOT "bloodless medicine." However, donated blood may be used to harvest blood components that may be used during some bloodless procedures.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Embolotherapy: Refers to various methods of blocking a bleeding blood vessel, preventing further blood loss. These include chemical agents that scar the inside of the blood vessel; mechanical agents that block a bleeding vessel, including metal coils and latex or silicone balloons; particles or microspheres, including gelatin foam; and injected liquid that quickly turns into a thicker gel-like or spongy mass to prevent bleeding from a vessel.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
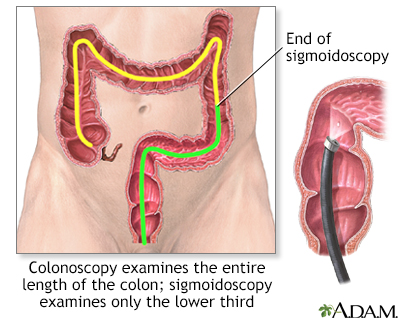
Endoscopy: A scope that can be used to visualize the inside of the body, either through insertion into a tiny incision or by passing the scope through a body opening (such as the mouth or anus). Endoscopy is used to examine, biopsy, or surgically treat a variety of conditions. Types of endoscopy include arthroscopy (joints); bronchoscopy (bronchial tubes, lungs); colonoscopy/sigmoidoscopy (large intestine); colposcopy (vagina, cervix); gastroscopy (stomach, small intestine); laparoscopy (abdomen); and others. Endoscopy is considered a "minimally invasive" procedure, which results in reduced bleeding. It is therefore a valuable bloodless medicine technique.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Erythropoietin: Erythropoietin is the name of a chemical normally produced by your body, primarily by your kidneys. Erythropoietin stimulates the bone marrow to produce red blood cells. Laboratory-made synthetic erythropoietin (e.g., Procrit, Epoetin alfa, Epogen, or Aranesp) may be administered prior to a bloodless surgery procedure in order to maximize your bone marrow's production of red blood cells. Other synthetic chemicals that mimic the activity of erythropoietin are in development.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Fibrin glue: A substance made from human clotting factors. These clotting factors can be harvested from donor blood plasma or from a patient's own blood plasma. Fibrin glue can be applied to a bleeding vessel. It both blocks the vessel from bleeding and activates normal clotting/coagulation activity. Because fibrin glue is made from blood products, each individual will need to examine their own conscience to decide if its use is personally acceptable.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Fluid expanders: Intravenous fluid solutions that are used to increase the volume of fluid in the circulating blood. The result is that when you bleed during surgery, your diluted blood contains a lower concentration of red blood cells.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Gamma knife: A high-tech surgical tool that can be used for brain surgery. This technique utilizes a powerful and precise form of radiation to destroy tumors or abnormal blood vessels with less blood loss than a traditional scalpel.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
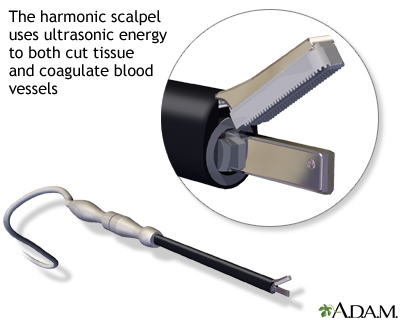
Harmonic scalpel: A surgical tool that uses ultrasound waves to cut tissue and seal bleeding vessels at the same time -- a helpful characteristic in transfusion-free surgery, because it helps keep blood loss to a minimum.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Hemodilution: The process of making blood more dilute than normal. The result is that when you bleed during surgery, your diluted blood contains a lower concentration of red blood cells.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
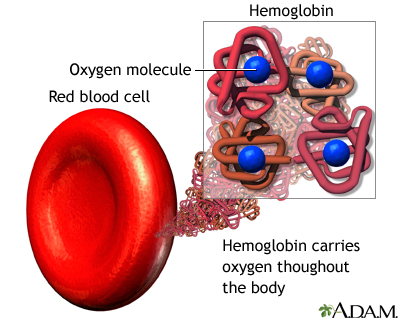
Hemoglobin: A chemical within red blood cells that allows oxygen to be carried throughout the body.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Hemophilia: A disease in which the blood clotting system is defective, resulting in an increased likelihood of serious bleeding after even minor injury.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
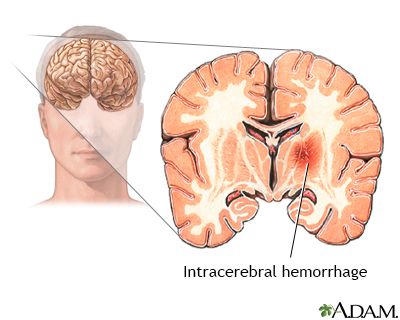
Hemorrhage: Heavy bleeding.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Hemostasis: To stop bleeding.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Hyperbaric: To be at higher-than-normal atmospheric pressure. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is used in some facilities to assist bloodless medicine in certain situations. You enter a chamber and breathe pressurized oxygen, which concentrates oxygen in your blood.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Hyperoxic: Having higher-than-normal oxygen saturation.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Hypotensive: Having low blood pressure. Hypotensive anesthesia is a technique that lowers a patient's blood pressure below normal during surgery. Blood loss tends to be slower when your blood pressure is low. However, blood pressure must be maintained at a particular threshold to ensure that all of your body's organs and tissues are receiving blood, so the practice of hypotensive anesthesia requires great skill and extraordinarily careful monitoring.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Intraoperative: During the course of an operation.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Iron: A nutrient that is required by your red blood cells for good oxygen-carrying capacity. Iron is important for bloodless surgery and can be obtained from dietary sources like red meat or through supplements, such as ferrous sulfate or ferrous gluconate.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Kidney dialysis: A procedure in which the blood is cleansed of toxins through an outside machine, replacing work that the kidneys normally do.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
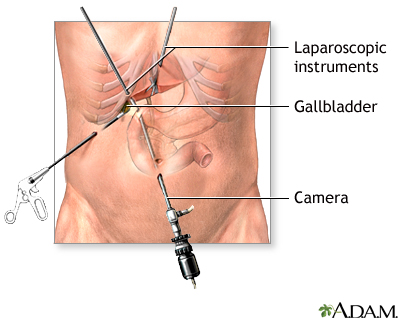
Laparoscopy: A surgical technique in which a lighted scope is inserted into a tiny incision in the abdomen. Laparoscopy can be used to visualize the inside of the abdomen for diagnosis, to retrieve tissue samples for biopsy, and to perform surgery using tiny instruments that are also passed into the abdomen through tiny "keyhole" incisions. Laparoscopy is considered a "minimally invasive" procedure, which results in reduced bleeding and may therefore be valuable for bloodless treatment of some conditions.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Laser surgery: A surgical technique that uses the energy from light to cut through tissues. It can reduce bleeding compared to traditional scalpels and may therefore be valuable for bloodless treatment of some conditions.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Major fractions: Blood products containing plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Jehovah's Witnesses do not accept major blood fractions as part of any treatment.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Mediastinal autotransfusion: A procedure performed most commonly after heart surgery, in which the fluids (including blood) that collect in the chest during and after surgery are collected and then given back to the patient through an IV.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
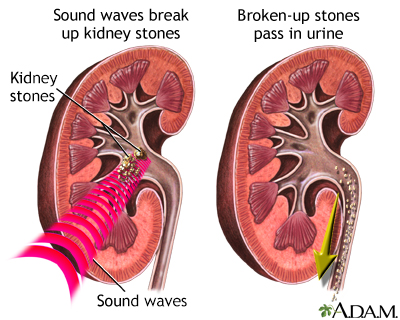
Minimally invasive surgery: Procedures that use small surgical cuts and holes, or no cuts at all. These methods can greatly reduce the amount of bleeding and are therefore of great importance to bloodless medicine. An example is endoscopy, which uses scopes inserted into small cuts or body openings. Another example is lithotripsy, which uses sound waves to break up a kidney or other stone into smaller bits, allowing it to pass out of the urinary system without having created any incision at all.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Minor fractions: Blood products containing clotting factors, albumin, growth factors, and immunoglobulins. Some Jehovah's Witnesses accept minor blood fractions as an individual "matter of conscience."
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Normothermia: Normal body temperature.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Normovolemia: All people maintain a particular volume of fluid circulating throughout their bodies; this is referred to as "normovolemia." During surgery, you will be given balanced intravenous solutions (volume expanders) to replace the fluids, salts, and sugars that you will invariably lose during the course of surgery.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
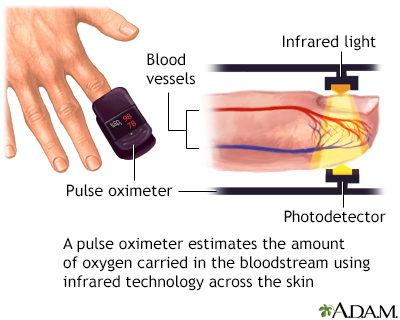
Oximeter: A device that monitors the amount of oxygen carried by the hemoglobin in red blood cells. In bloodless medicine, any blood a patient loses is not replaced by transfusion, so it is extremely important to monitor how much oxygen the patient's body is receiving from the remaining blood.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Plasma: The fluid component of blood, in which the various types of blood cells are suspended. Jehovah's Witnesses consider plasma to be a major blood fraction and do not consider it to be an acceptable part of treatment.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Plasmapheresis: A type of apheresis that is used to separate plasma from blood. Blood is removed from a donor, the plasma is harvested and retained, and the donor's blood cells are returned to him or her. Plasmapheresis may also be performed on a patient's own blood as a treatment for certain conditions.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
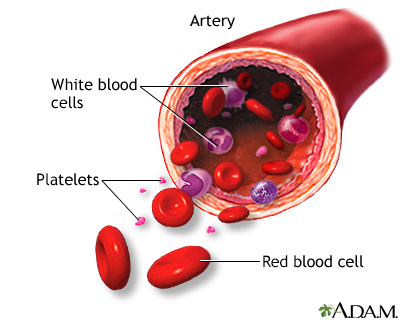
Platelet: A component of blood responsible for blood clotting at the point of an injury to a blood vessel. Without platelets, our blood would not be able to clot and hemorrhaging or uncontrolled bleeding would result. Platelets are considered a major blood fraction and are not acceptable to Jehovah's Witnesses as part of any treatment.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Platelet gel: A concentrate made from a patient's own blood plasma, mixed with calcium and clotting compounds produced in cows. Platelet gel concentrates can be applied during the course of surgery to control bleeding. As with fibrin glue, platelet gel concentrates are produced from plasma, so their use by some individuals is a matter of conscience.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Primary blood components: Red cells, white cells, plasma, and platelets (also called major fractions). Jehovah's Witnesses do not accept primary blood components (major fractions) as part of any treatment.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Procuren solution: A solution made from an individual's own blood. The growth factors in the patient's own platelets are harvested, and reproduced in a laboratory to create the procuren solution. This solution is then applied to a wound to improve healing capacity and shorten duration of healing.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
RBC nuclear scan: A test in which the individual's own red blood cells are harvested, tagged with radioactive material, and then returned to the individual. Imaging scans are then performed that will highlight areas of bleeding, because the tagged red blood cells will be seen leaking from these areas.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Scalpel: Originally, a scalpel was a very sharp, small knife used to perform surgery. Now a scalpel can use a variety of energy sources to cut through tissue, including light (laser scalpel), microwaves (microwave-coagulating scalpel), ultrasonic energy (ultrasonic and harmonic scalpels), and radiation (gamma knife).
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Stereotactic/Stereotaxic: A technique for locating the exact area needing treatment by using advanced imaging techniques that verify the three-dimensional coordinates of the abnormal area. By pinpointing the exact area, the surgeon can minimize the amount of cutting (and hence bleeding) that occurs during surgery.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
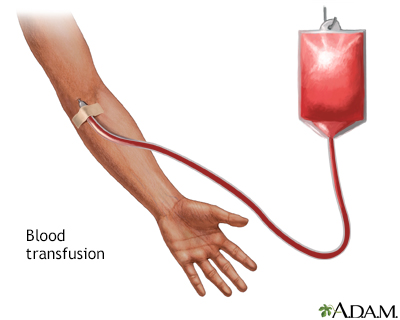
Transfusion: The delivery of blood products to an individual to replace blood that is lost during surgery or from injury. The blood or blood products are usually donated anonymously or through blood banking, then stored until the time they are needed. At that point, the blood products are administered through an intravenous (IV) line into a patient's vein. A blood transfusion is what bloodless medicine seeks to avoid.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Ventilation: To provide a patient with oxygen.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
WBC nuclear scan: A test in which an individual's own white blood cells are harvested, tagged with radioactive material, and then returned to the individual. Imaging scans are then performed that will highlight areas of infection, because the tagged white blood cells will migrate to these areas.
|
Review Date:
6/28/2011 Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Palm Beach Cancer Institute, West Palm Beach, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc. |

