| Step 2: The health risks of obesity |
If you are morbidly obese, you have a much greater risk of developing a variety of serious medical conditions compared to individuals who are not obese. You may develop health problems at a younger age. Some of these conditions may include:
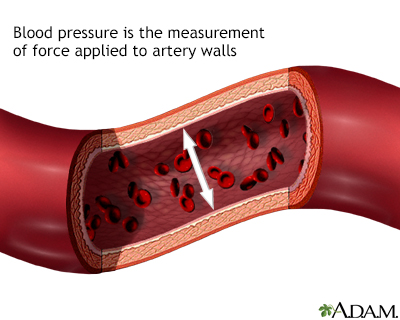
High blood pressure
High blood pressure is more common in obese adults.
High cholesterol
Overweight people often have too much cholesterol and other fats in their blood. High cholesterol is linked to angina (a type of chest pain related to narrowing of the arteries that feed the heart), heart disease, heart attack, and stroke.

Type 2 diabetes
Gaining as little as 11 - 18 pounds doubles your chance of developing type 2 diabetes. More than 80% of people with diabetes are classified as overweight or obese.
Arthritis
Your risk of arthritis increases by 9 - 13% for every 2 pounds of weight that you gain.
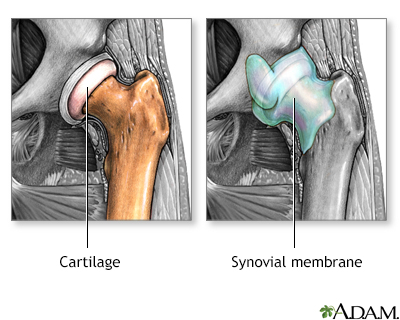
| Osteoarthritis is a deterioration of cartilage and overgrowth of bone often due to "wear and tear." Rheumatoid arthritis is the inflammation of a joint's connective tissues, such as the synovial membranes, which leads to the destruction of the articular cartilage. |
Breathing problems
Asthma and obstructive sleep apnea are more common in obese people.
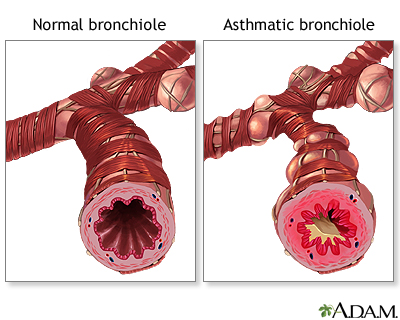
| During an asthma attack, smooth muscles located in the bronchioles of the lung constrict and decrease the flow of air in the airways. The amount of air flow can further be decreased by inflammation or excess mucus secretion. |
Cancer
Obesity may increase the risk of endometrial, breast, prostate, kidney, esophageal, and colon cancers. Women who gain more than 20 pounds between the age of 18 and midlife have double the risk of developing breast cancer after menopause.
Pregnancy complications
Obesity increases the risk of diabetes during pregnancy, pre-eclampsia, delivery complications, and birth defects. Obese women have 10 times the risk of high blood pressure during pregnancy. Women who are obese and their babies have an increased risk of death during pregnancy.
Premature death
About 300,000 deaths a year are due to the consequences of obesity. Obese people have a 50 - 100% increased risk of premature death.
Obesity is also linked to heart failure, back pain, bladder problems, gallstones, kidney stones, liver disease, gout, complications and infections after surgery, and menstrual irregularity and infertility in women.
Obesity can hamper your ability to get around. It can complicate your life with self-esteem and discrimination issues, and may lead to depression and eating disorders.
Take action now
The issues at stake are not about physical appearance. Morbid obesity is a life-threatening medical condition. Gaining control over this serious health problem requires a commitment of your time, attention, energy and efforts. Use the following suggestions to help get you on the right path:
- Define the nature of the problem. Are you overweight? Obese? Morbidly obese?
- Ask your physician to help you determine other risk factors you might have for developing serious medical diseases.
- Develop a plan of attack to control all areas of your life that might be contributing to weight and health problems.
- Use every possible method in your fight against obesity, including dietary changes, physical activity, and medical expertise.
- Schedule a medical consultation to help you determine your next steps.
|
Review Date:
12/16/2012 Reviewed By: Robert A. Cowles, MD, Associate Professor of Surgery, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. |
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
