Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT)
Definition
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) is episodes of a rapid heart rate that start in a part of the heart above the ventricles. "Paroxysmal" means from time to time.
Alternative Names
PSVT; Supraventricular tachycardia; Abnormal heart rhythm - PSVT; Arrhythmia - PSVT; Rapid heart rate - PSVT; Fast heart rate - PSVT
Causes
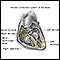
Normally, the chambers of the heart (atria and ventricles) contract in a coordinated manner.
- The contractions are caused by an electrical signal that begins in an area of the heart called the sinoatrial node (also called the sinus node or SA node).
- The signal moves through the upper heart chambers (the atria) and tells the atria to contract.
- After this, the signal moves down in the heart and tells the lower chambers (the ventricles) to contract.
The rapid heart rate from PSVT may start with events that occur in areas of the heart above the lower chambers (ventricles).
There are a number of specific causes of PSVT. It can develop when doses of the heart medicine, digitalis, are too high. It can also occur with a condition known as Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, which often causes symptoms in young people and infants.
The following increase your risk for PSVT:
- Alcohol use
- Caffeine use
- Illicit stimulant drug use
- Smoking
Symptoms
Symptoms most often start and stop suddenly. They can last for a few minutes or several hours. Symptoms may include:
- Anxiety
- Chest tightness
- Palpitations (a sensation of feeling the heartbeat), often with an irregular or fast rate (racing)
- Rapid pulse
- Shortness of breath
Other symptoms that can occur with this condition include:
Exams and Tests
A physical exam during a PSVT episode will show a rapid heart rate. It may also show forceful pulses in the neck.
The heart rate may be over 100, and even more than 250 beats per minute (bpm). In children, the heart rate tends to be very high. There may be signs of poor blood circulation such as lightheadedness. Between episodes of PSVT, the heart rate is normal (60 to 100 bpm).
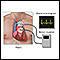
An electrocardiogram (ECG) during symptoms shows PSVT. An electrophysiology study (EPS) may be needed for an accurate diagnosis and to find the best treatment.
Because PSVT comes and goes, to diagnose it people may need to wear a 24-hour Holter monitor. For longer periods of time, another type of the rhythm recording device may be used.
Treatment
PSVT that occurs only once in a while may not need treatment if you don't have symptoms or other heart problems.
You can try the following techniques to interrupt a fast heartbeat during an episode of PSVT:
- Valsalva maneuver. To do this, you hold your breath and strain, as if you were trying to have a bowel movement.
- Coughing while sitting with your upper body bent forward.
- Splashing ice water on your face
You should avoid smoking, caffeine, alcohol, and illicit drugs.
Emergency treatment to slow the heartbeat back to normal may include:
- Electrical cardioversion, the use of electric shock
- Medicines through a vein
Long-term treatment for people who have repeat episodes of PSVT, or who also have heart disease, may include:
- Cardiac ablation, a procedure used to destroy small areas in your heart that may be causing the rapid heartbeat (currently the treatment of choice for most PSVTs)
- Daily medicines to prevent repeat episodes
- Pacemakers to override the fast heartbeat (on occasion may be used in children with PSVT who have not responded to any other treatment)
- Surgery to change the pathways in the heart that send electrical signals (this may be recommended in some cases for people who need heart surgery for other reasons)
Outlook (Prognosis)
PSVT is generally not life threatening. If other heart disorders are present, it can lead to congestive heart failure or angina.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- You have a sensation that your heart is beating quickly and the symptoms do not end on their own in a few minutes.
- You have a history of PSVT and an episode does not go away with the Valsalva maneuver or by coughing.
- You have other symptoms with the rapid heart rate.
- Symptoms return often.
- New symptoms develop.
It is especially important to contact your provider if you also have other heart problems.
References
Dalal AS, Van Hare GF. Disturbances of rate and rhythm of the heart. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 462.
Kalman JM, Sanders P. Supraventricular tachycardias. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 65.
Page RL, Joglar JA, Caldwell MA, et al. 2015 ACC/AHA/ HRS guideline for the management of adult patients with supraventricular tachycardia: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2016;133(14);e471-e505. PMID: 26399662 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26399662/.
Zimetbaum P, Goldman L. Supraventricular ectopy and tachyarrhythmias. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 52.
|
Review Date:
2/27/2024 Reviewed By: Thomas S. Metkus, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine and Surgery, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |