| Step 8: Drug delivery devices |
There are several ways to get an asthma drug into your lungs. The most common methods are:
- Metered Dose Inhalers (MDI) with or without a spacer
- Dry Powder Inhalers
- Nebulizers
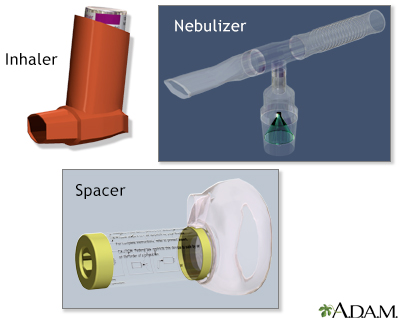
Each of the methods has a few pros and cons, but all are effective. Nebulizers are not as commonly used at home as they were in the past. The method to use is partly a matter of personal preference, but it also depends on your age, ability to use MDIs, and the drugs you have been prescribed. Many people find that it is easier to get the full dose of medicine when they use a spacer along withthe MDI.
An MDI with a spacer is the most common method. Some people, however, use multiple methods, such as using a nebulizer while relaxing at home and an MDI when they are "on the go."
Asthma drugs can also be delivered as pills, capsules, liquids, or injections, but these methods are not routinely used for most patients. They require the drug to be absorbed into the bloodstream before making its way to the lungs, and therefore require higher doses. These methods are more likely to have side effects and take longer for the drug to work. Usually, only people with moderate-severe persistent asthma are considered for regular use of oral medications (pills and liquids). On type of medication, called a leukotriene inhibitor, may be used as a routine controller medicaton under certain circumstances.
 |
|
Reviewed By: Allen J. Blaivas, DO, Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine UMDNJ-NJMS, Attending Physician in the Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, Department of Veteran Affairs, VA New Jersey Health Care System, East Orange, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Previoulsy reviewed by David A. Kaufman, MD, Section Chief, Pulmonary, Critical Care & Sleep Medicine, Bridgeport Hospital-Yale New Haven Health System, and Assistant Clinical Professor, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. (6/1/2010)
