
Heartburn medications
Introduction
The purpose of this tool is to help you decide whether GERD medication is right for you. When making a decision like this, you must balance:
- The reasons for taking the medication
- The potential health risks, side effects, or limitations of the medication
- Whether there are alternative treatments that may be more appropriate
- Cost
This tool is not a substitute for professional medical care and advice. Work with your doctor to help you make this decision. A second opinion from another doctor may be valuable. Medication always has potential side effects, and you should be fully informed about the risks and benefits of this type of medication. There is usually no exact "right" or "wrong" answer.
Your doctor may make certain recommendations to you. However, the final decision about whether to use this medication rests with you.
What is the medication?
Heartburn is a painful burning sensation in the esophagus, just below or behind the breastbone. The pain often rises in your chest and may radiate to your neck or throat. Almost everyone has occasional heartburn. If you have frequent, ongoing heartburn, you may have gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
GERD occurs when food or liquid travels from the stomach back up into your esophagus (the tube from the mouth to the stomach). This material is acidic and can irritate the esophagus, often causing heartburn and other symptoms.
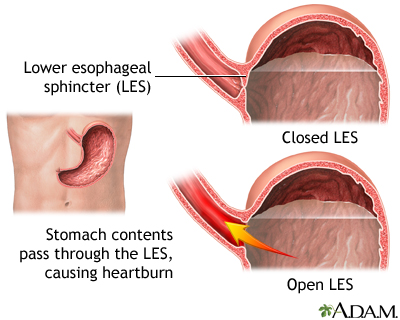
You can take many steps before taking medication. These include changing the foods you eat and losing weight. Your doctor can explain many of the steps that can help.
If you continue to have problems, you might consider medication. Several different kinds of medicine are available over-the-counter. Your doctor may also suggest prescription medicine.
Key points
- Medications for GERD include antacids (Rolaids, Tums), H2 blockers (Pepcid AC, Tagamet, and Zantac), and proton-pump inhibitors (such as Prilosec).
- Antacids neutralize digestive acids and are the primary drugs for mild symptoms.
- H2 blockers inhibit acid secretion for six to 24 hours and are very useful for people who need persistent acid suppression. They may also prevent heartburn episodes in people who are able to predict its occurrence.
- Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) suppress the production of stomach acid. Studies report significant relief from PPIs in most patients with heartburn.
- GERD medicines may help prevent the serious damage associated with GERD.
- Medication can decrease the chance of developing a scarred esophagus that can lead to food becoming trapped at the end of the esophagus.
- GERD medicines are safe and effective, with the only side effects being rare headache and diarrhea.
How much time this decision tool will take
5 - 10 minutes
What this tool will provide
- A personalized list of factors for you to weigh
- Questions to ask your doctor
- Alternatives to this medication
- Recommended reading
|
Review Date:
9/19/2010 Reviewed By: David C. Dugdale, III, MD, Professor of Medicine, Division of General Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc. |
- Coron E, Hatlebakk JG, Galmiche JP. Medical therapy of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2007 Jul;23(4):434-9. Review.
- DeVault KR, Castell DO. American College of Gastroenterology. Updated guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2005 Jan;100(1):190-200.
- Moayyedi P, Talley NJ. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Lancet. 2006 Jun 24;367(9528):2086-100. Review.
- Orlando RC. Diseases of the esophagus. Goldman L, Ausiello D, eds. Cecil Textbook of Medicine. 23rd ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2007:chap 140


