| Contact dermatitis |
Contact dermatitis refers to a range of reactions that result from skin contact with a foreign substance. It may appear as an itchy, red, swollen, or blistery rash after contact with an allergen or irritant. Contact dermatitis is commonly seen in occupational settings.
Most cases of contact dermatitis occur on the hands. Once you get the offending substance on your hands, it's easy to cause further irritation on other parts of the body that you touch.
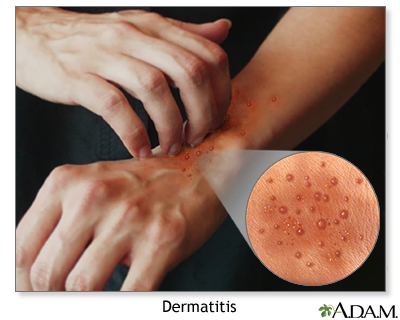
| Contact dermatitis refers to a range of reactions that result from skin contact with a foreign substance. The reaction on the skin as seen above is one of several possible appearances of contact dermatitis. |
Allergic vs. irritant contact dermatitis
About 20% of contact dermatitis cases result from allergic reactions -- the rest are caused by irritants, like chemicals in an industrial workplace (although some chemicals can be allergens too).
Allergic and irritant contact dermatitis can be difficult to distinguish, because the resulting rashes are very similar. The pattern and location of the rash on the skin help distinguish whether it was caused by an allergen or irritant. Irritant contact dermatitis usually appears on the hands within minutes after touching the offending irritant, and is usually more painful than itchy. With allergic contact dermatitis, an itchy rash usually appears within 24 - 48 hours on the exact part of the body that contacted the allergen, as with poison ivy. Some people may develop contact dermatitis allergy that doesn't cause problems until many repeated exposures.
Causes
Irritant contact dermatitis is often caused by soaps, detergents, and other cleaners (like bleach) as well as formalin, latex, and certain antimicrobial skin ointments.
Causes of allergic contact dermatitis include urushiol (a chemical in poison ivy, poison oak, and mango), nickel in hairpins, earrings, zippers, door handles, and ingredients in hair dyes, insecticides, fungicides, and rubber products. Most of these substances are not routinely included in allergy testing. They need to be tested using a patch test.
Symptoms
The reaction varies depending on which body part is affected. The most sensitive parts of the body are the eyelids, genitalia, and neck. The least sensitive are the palms, soles, and scalp.
Irritants can cause itching, pain, stinging, burning, redness, heat, swelling, and tenderness. Some potent irritants can cause reactions that resemble burns.
With allergic reactions, the most common symptom is severe itching. Blistering and redness may also occur.
Diagnosing contact dermatitis
To help determine what caused your rash, your doctor will ask what you were doing prior to noticing it. He or she will ask questions about your age and occupation, your recent hobbies and sports activities, your use of chemicals at home or work, and your use of cosmetics. The doctor will also ask about your family history of allergies, previous allergic reactions, history of skin conditions, and any medications you take. The doctor may also ask if there have been any recent changes in your household, such as new cleaning products or detergents.
If you suspect that your rash is due to an allergy, your doctor can confirm it by testing your skin with a small amount of the suspected allergen.
Treatment
Usually, contact dermatitis goes away within 3 - 4 weeks after contact with the allergen. The inflamed skin can be treated with cold compresses, unscented oils or lotions, baths with oatmeal bath or bath oils, and calamine lotion to relieve the itching and burning that accompany dermatitis. For severe cases, your doctor may recommend corticosteroids to diminish the inflammation. The best treatment is to avoid contact with the substance causing the reaction.
Reviewed By: Paula J. Busse, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of Clinical Immunology, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, NY, Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
